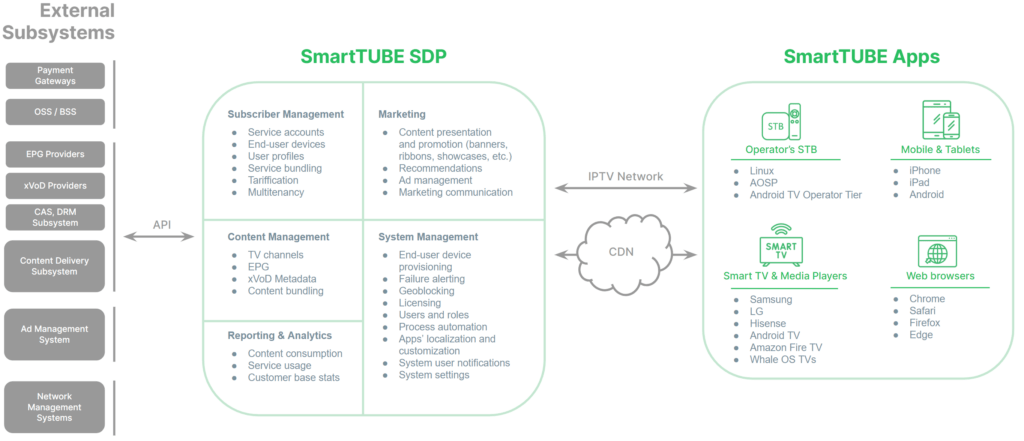
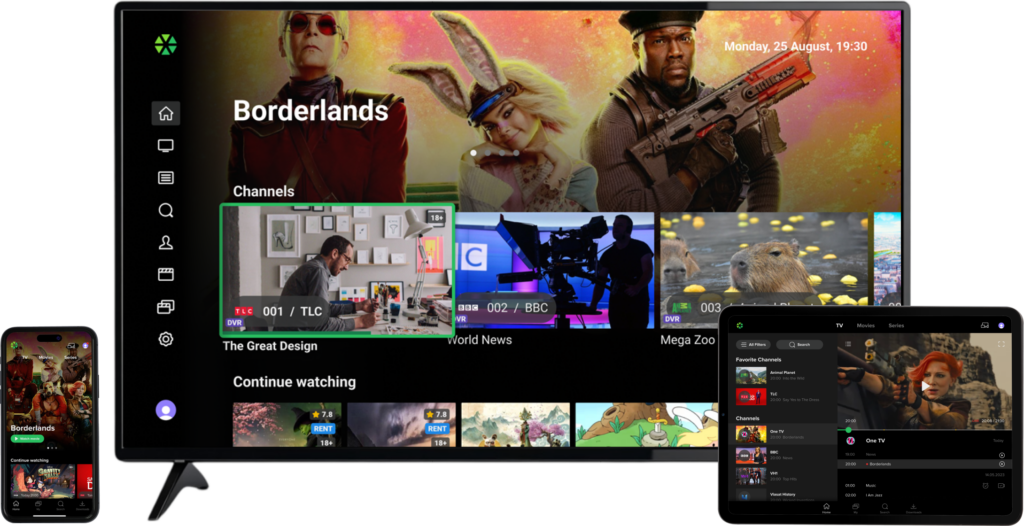
SmartTUBE Apps are a range of user-friendly and highly customizable applications compliant with the most current streaming industry standards. Tailored for popular device platforms, these applications seamlessly integrate established user interaction patterns to offer a superior viewing and application experience. Users have access to a diverse content selection, including live TV, video-on-demand, catch-up TV, nPVR, and shared TV recordings.
Note: As we continually enhance the UI and UX of SmartTUBE Apps, please note that the screenshots below might not reflect the latest versions.
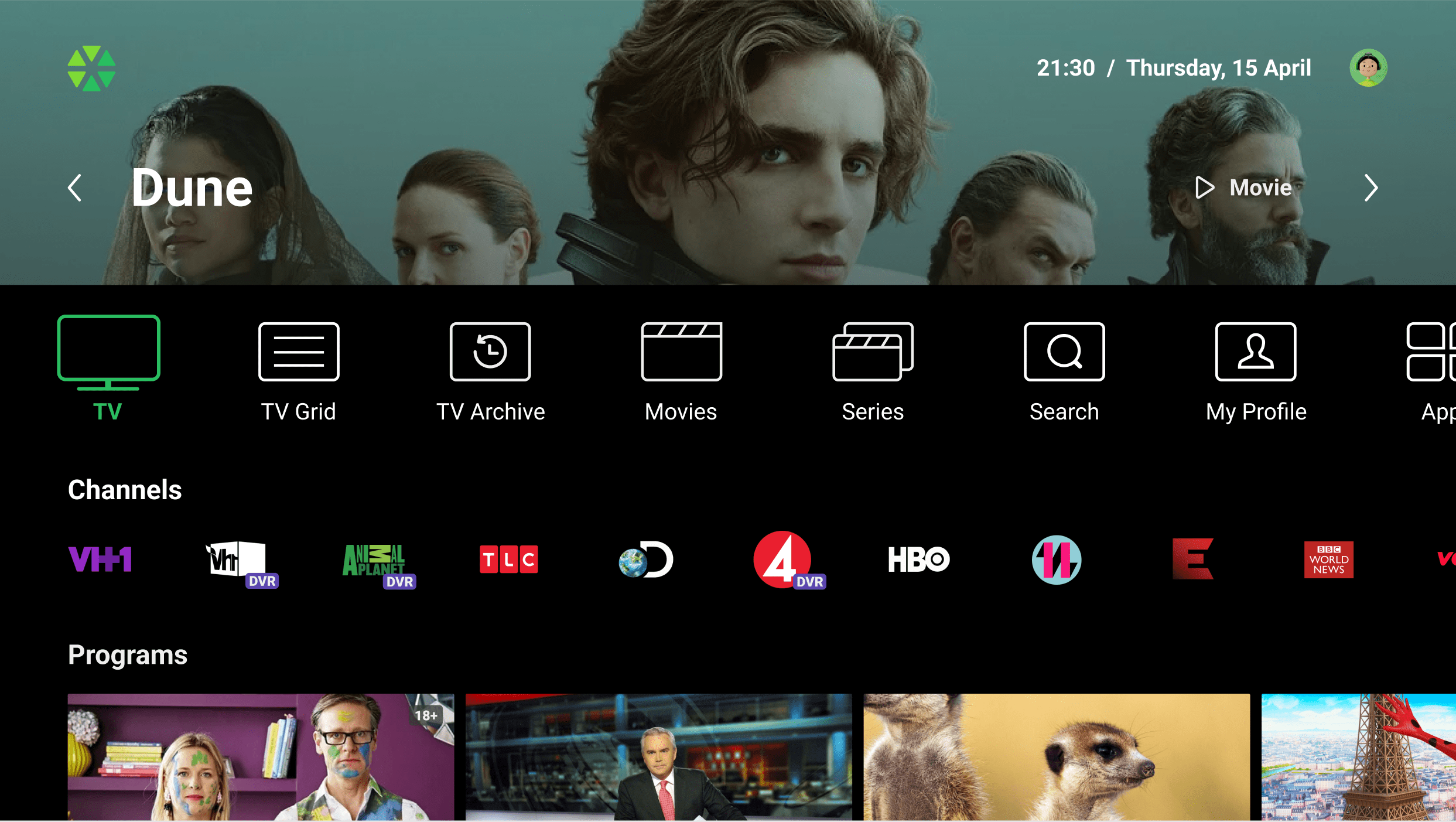
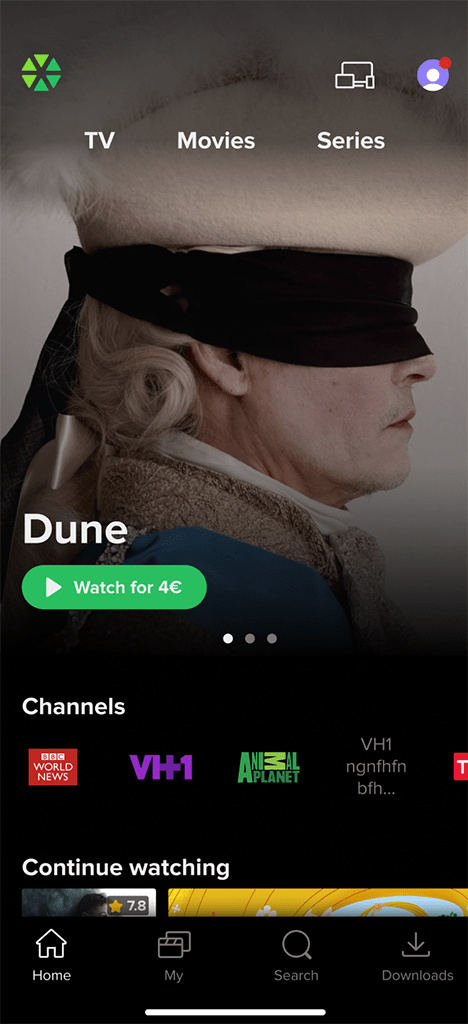
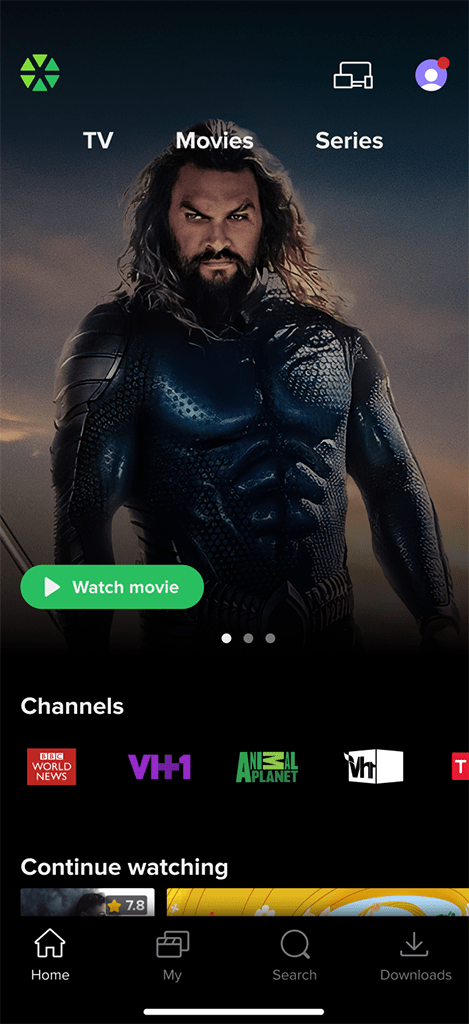
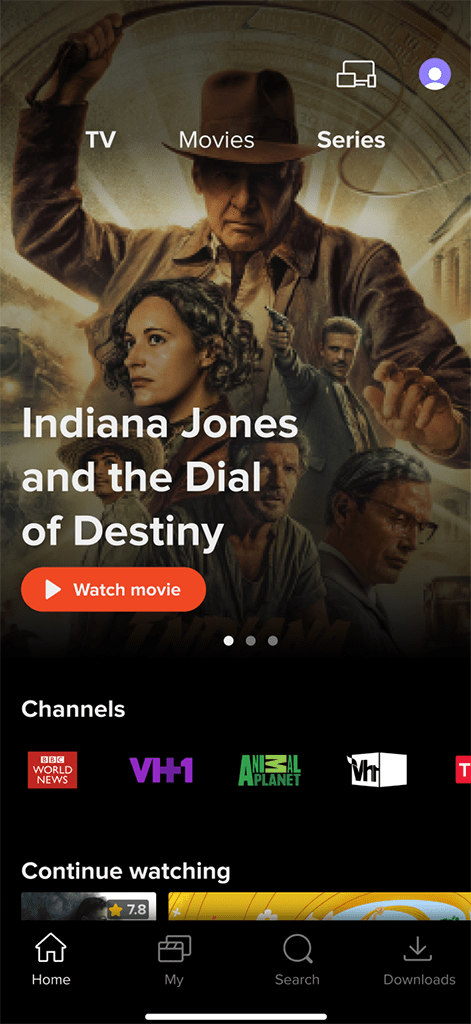
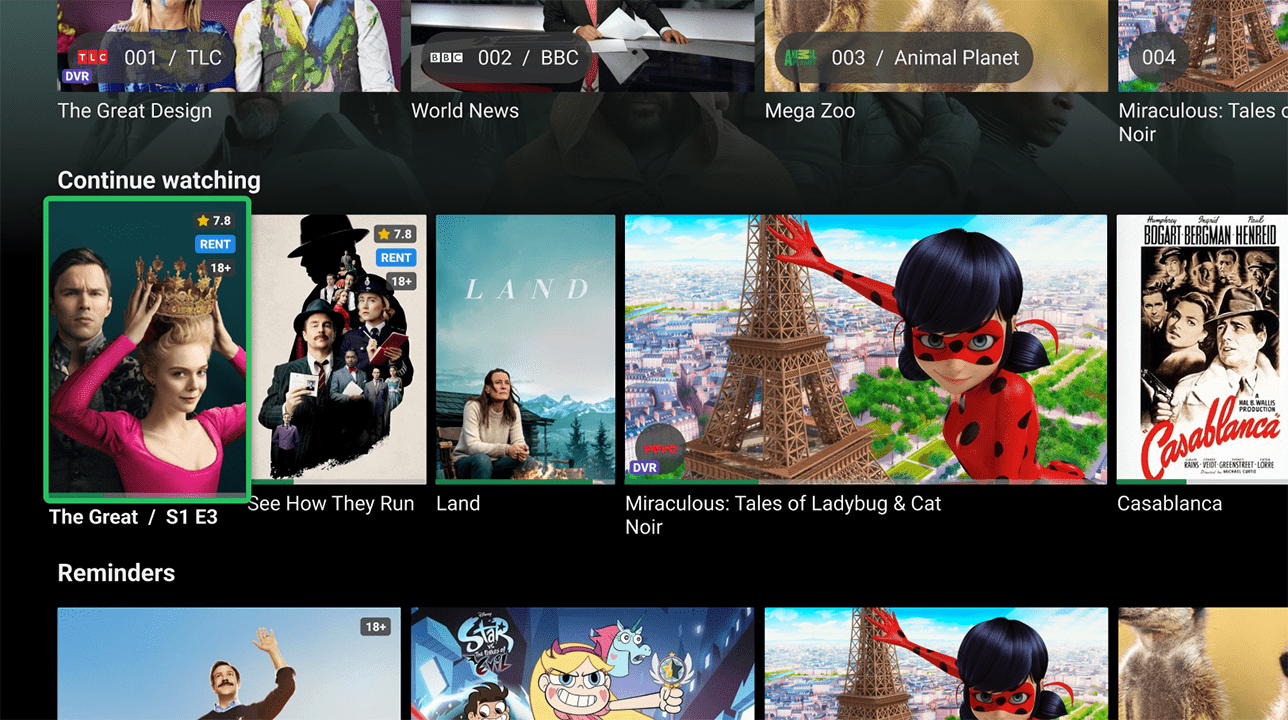
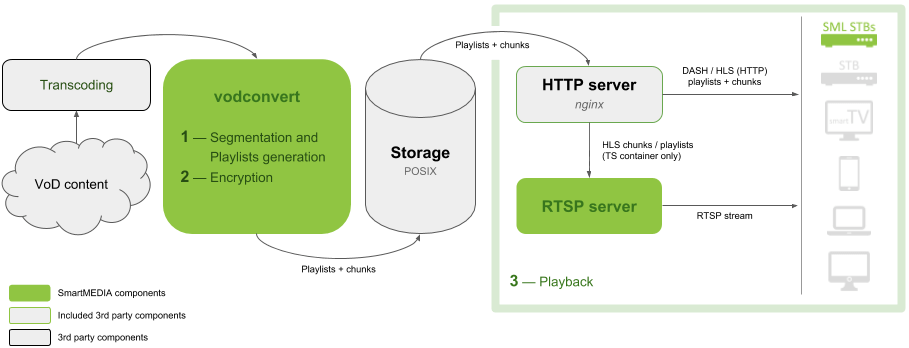
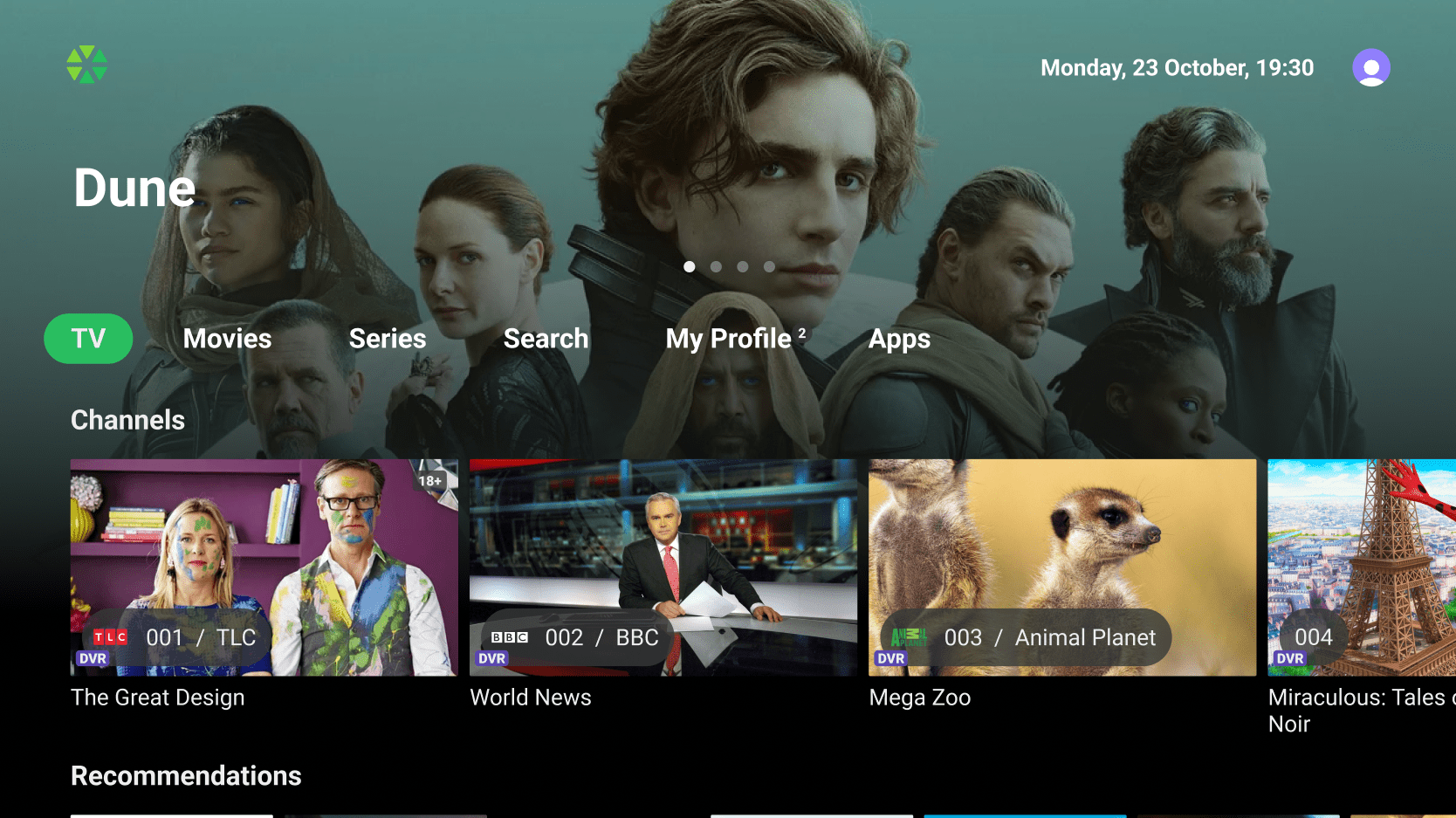
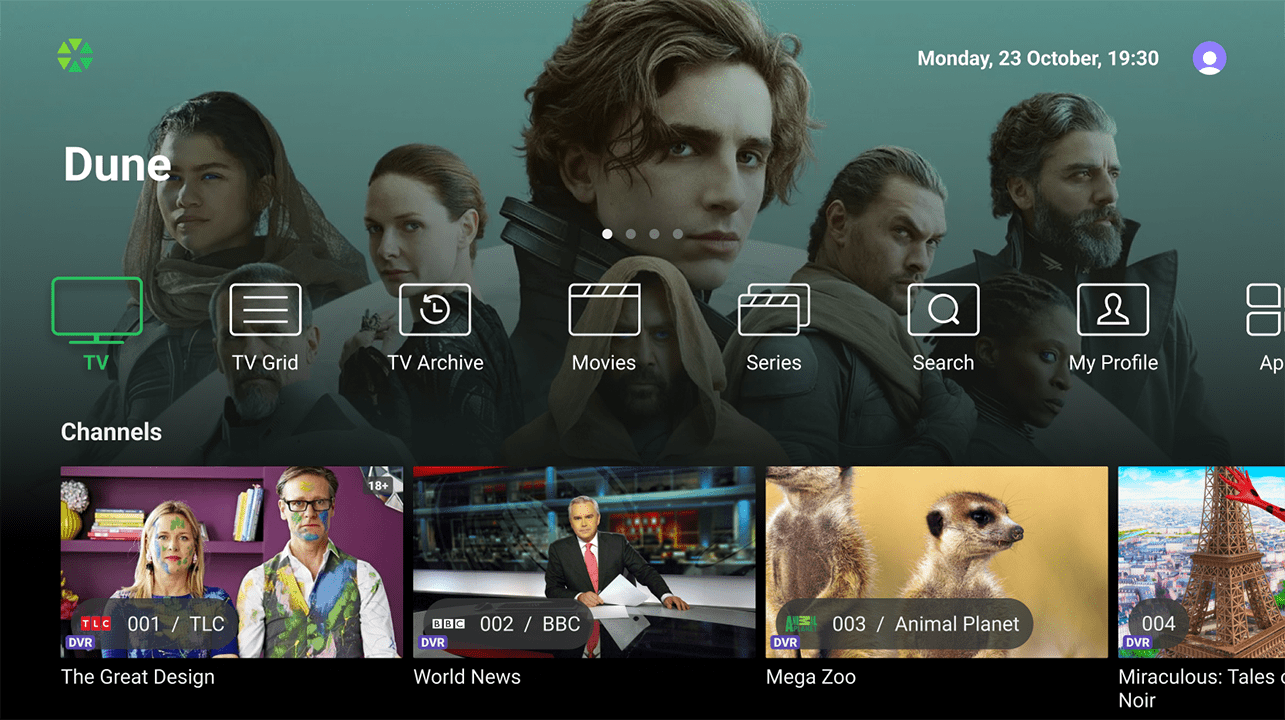
Home Screen
The Home screen is the first screen the user sees after loading the app or hitting the ‘Home’ button. Operators can customize it’s layout by managing Top banner, Main menu, and a set of Content rails.
Top Banner
Operator can choose one of the following options to display the Top banner:
- Regular banner: A regular opaque banner with a clear bottom edge, not overlapped by any other UI elements.
- Faded banner: An opaque banner with a faded bottom edge typically overlapped by the main menu and first content rail. Optionally, the faded banner can automatically play the movie trailer after a set amount of time when it is in focus.
Main Menu
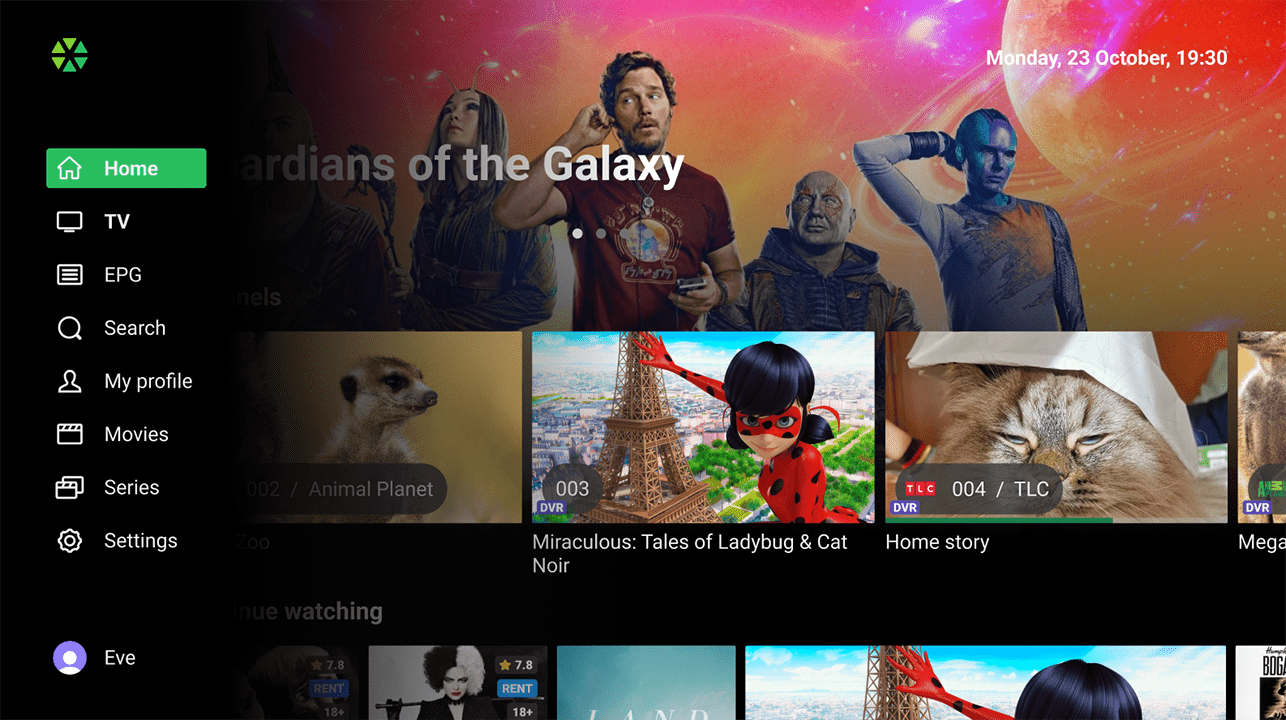
The Main menu on large-screen devices can be displayed in either a vertical or horizontal arrangement. For horizontal layouts, menu items can be enhanced with icons or presented as plain text. The Main menu may include the following items:
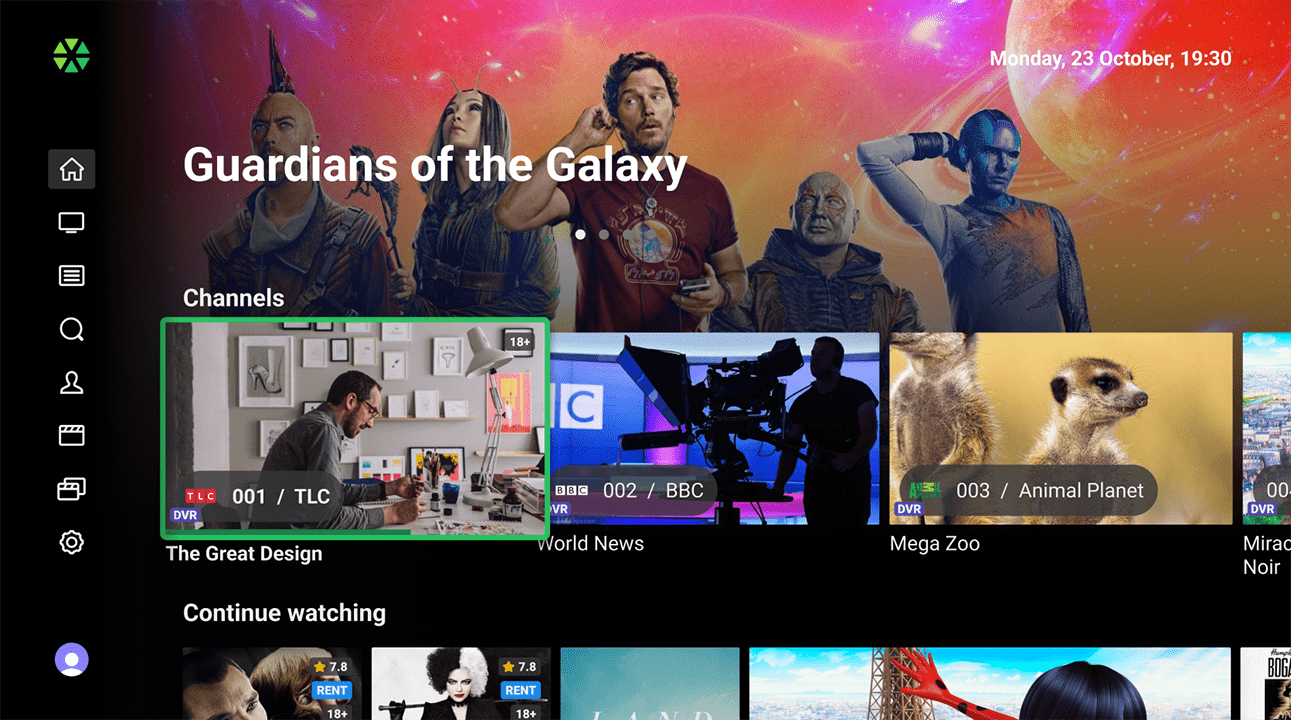
- TV: Displays channels and programs as a vertical scrollable list for easy navigation. Includes detailed information about current broadcasts, channel guides, and completed/upcoming programs with description and screenshot.
- EPG: Displays a classic EPG grid showcasing TV programs’ durations on a horizontal timeline. Users can to select a program for additional information and functions, with a window displaying the current broadcast.
- Search: Allows to search through all types of content, displaying TV programs and VoD content on one screen.
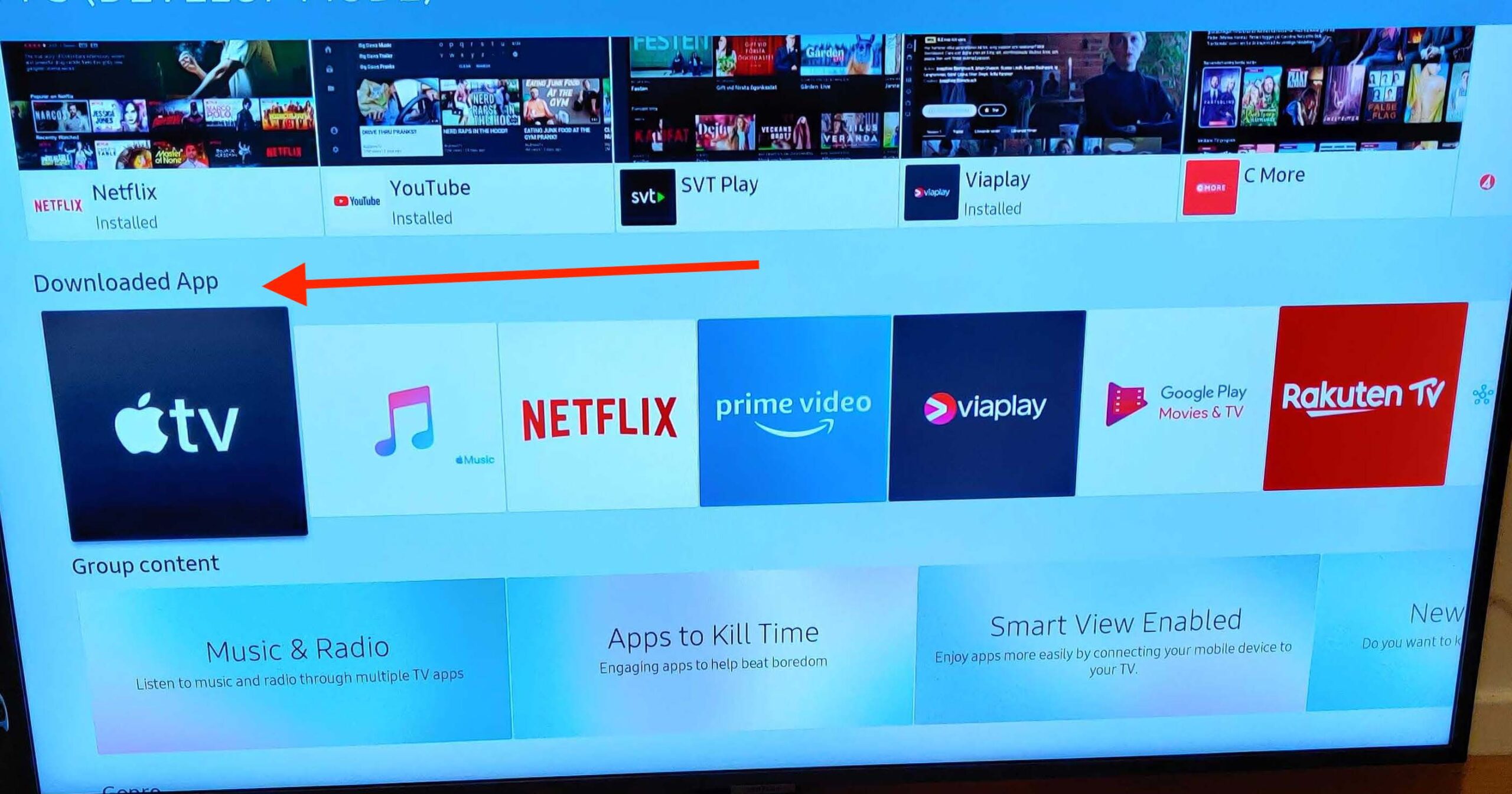
- Movies: Displays the movie library with posters and titles in a mosaic view or as a list of content rails.
- TV Series: Displays the series library featuring posters and titles presented in either a mosaic view or themed rails list. Each poster serves as a visual representation of a series, enabling users to delve into a series card. From there, subscribers can choose the desired season and episode for viewing.
- Radio: Opens the list of IP radio stations available for listening.
- My [operator name]: Allows a subscriber to access personalized content such as watch history, favorite channels and movies, personal recordings, reminders, and purchased movies.
- Applications: Provides access to the library of Android apps available on Android TV / Android STB devices, if the SmartTUBE App acts as a launcher.
- Settings: Provides access to the user profile settings and system settings (time zone, network settings, video output modes, etc.).
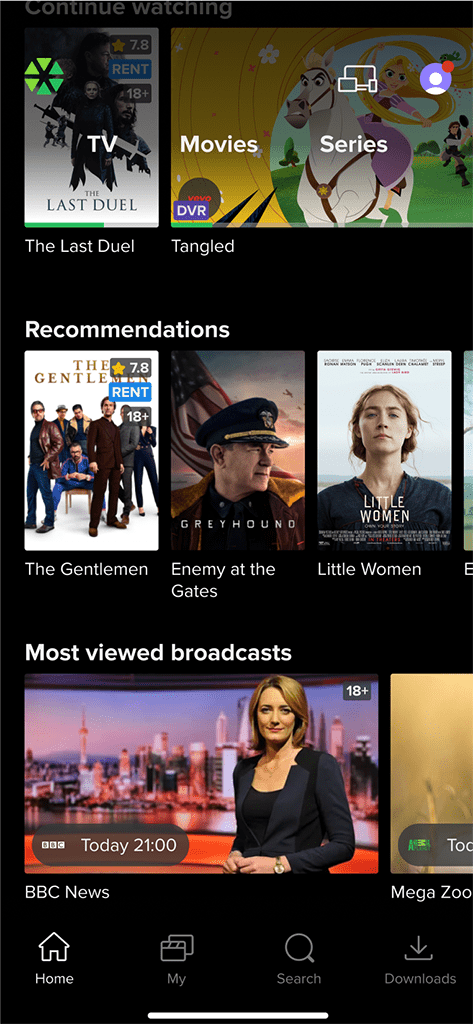
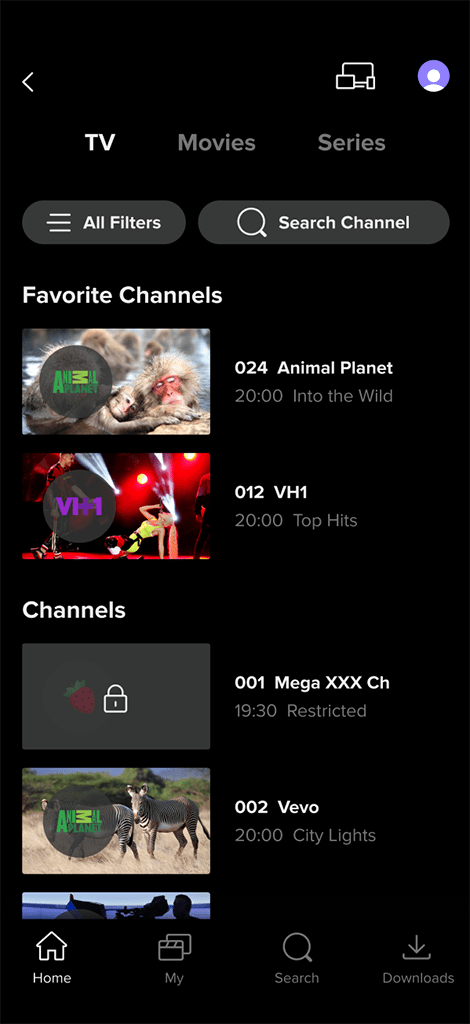
The main menu on mobile devices typically includes the following items: Home, My, Search, and Downloads. The Downloads section allows users to access content that has been downloaded for offline viewing. Additionally, users can navigate to the TV, Movies, and Series pages using the top menu located on the Home screen.
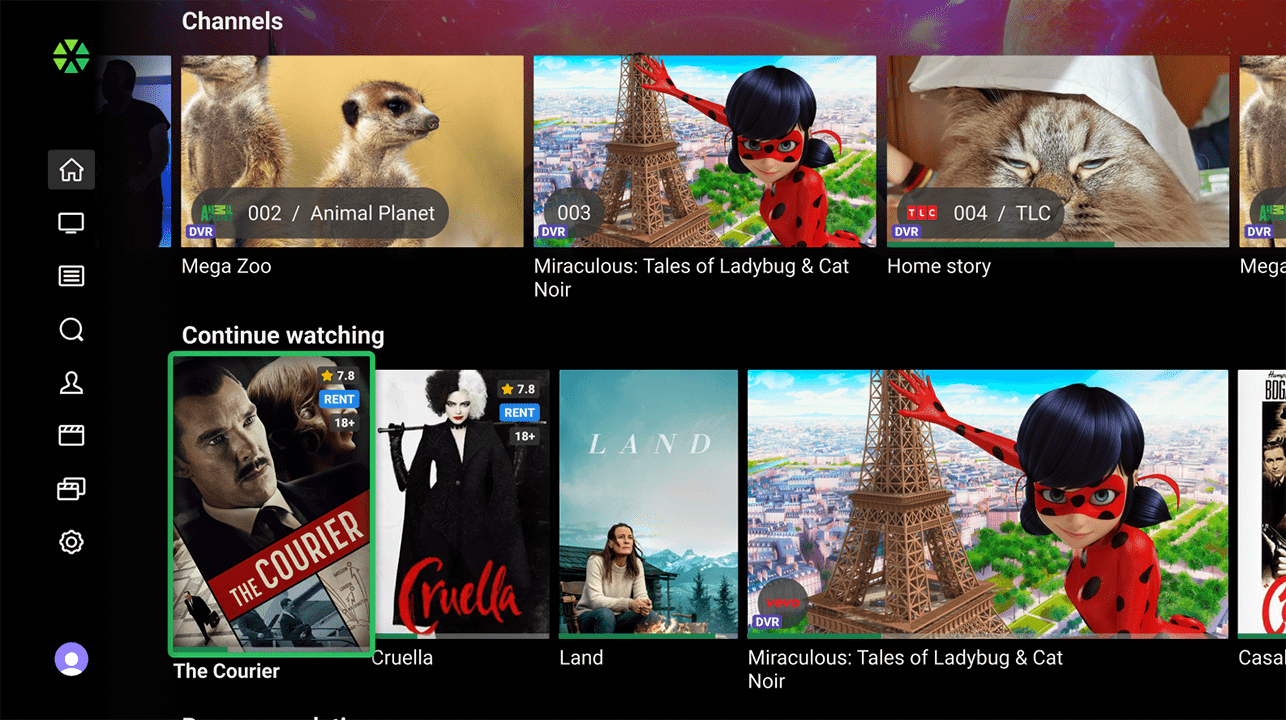
Content Rails
Operators have the ability to populate the content pages (Home, Movies, Series, and My Profile) with an unlimited number of predefined and custom Content rails:
- TV Channels: Display of TV channels presented as posters of currently streaming programs. User-favorited channels are prioritized, followed by operator-sorted channels.
- Manually recommended content: Curated xVoD content or TV programs manually selected by the operator.
- Auto recommended content: Automatically generated xVoD content based on user viewing history, leveraging the SmartTUBE Recommender module.
- Top 10 TV programs: Compilation of the most popular TV programs viewed by all subscribers.
- Applications: List of integrated applications defined by the operator. Available only for the Android TV / STB devices, if the SmartTUBE App is a launcher.
- Continue watching: List of xVoD content and TV programs that the user has not finished watching.
- Watch history: Chronological listing of xVoD content and TV programs watched by the user.
- Favorite channels: Channels marked as favorites by the user.
- Favorite movies: Movies marked as favorites by the user.
- Personal recordings: Recordings of TV programs initiated by the user within the nPVR service.
- Reminders: Alerts for upcoming TV programs set by the user.
- Purchased movies: List of xVoD content purchased by the subscriber.
- Custom rails: Operator-filtered xVoD content or TV programs based on various content and subscriber’s account attributes (for example, French comedies of 80-th, Modern Bollywood movies, Jackie Chan action movies, etc.). The filtered TV programs and xVoD content can be sorted by various attributes.
TV-related Content
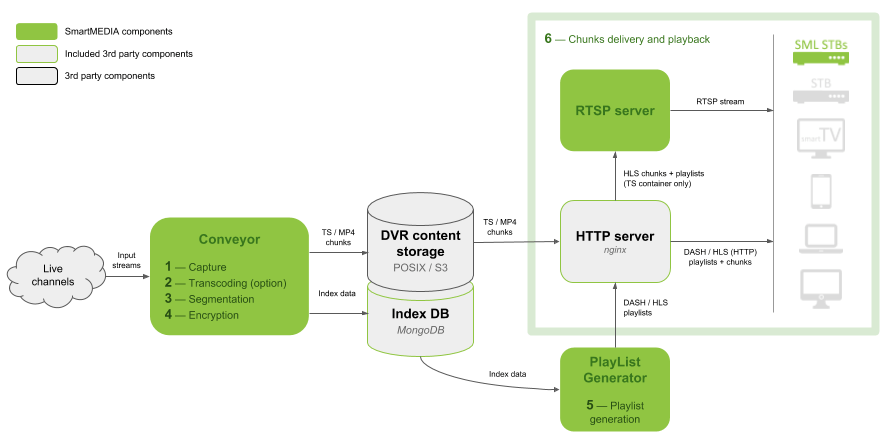
SmartTUBE Apps provide users with access to the comprehensive functionalities offered by the SmartTUBE solution for TV-related services:
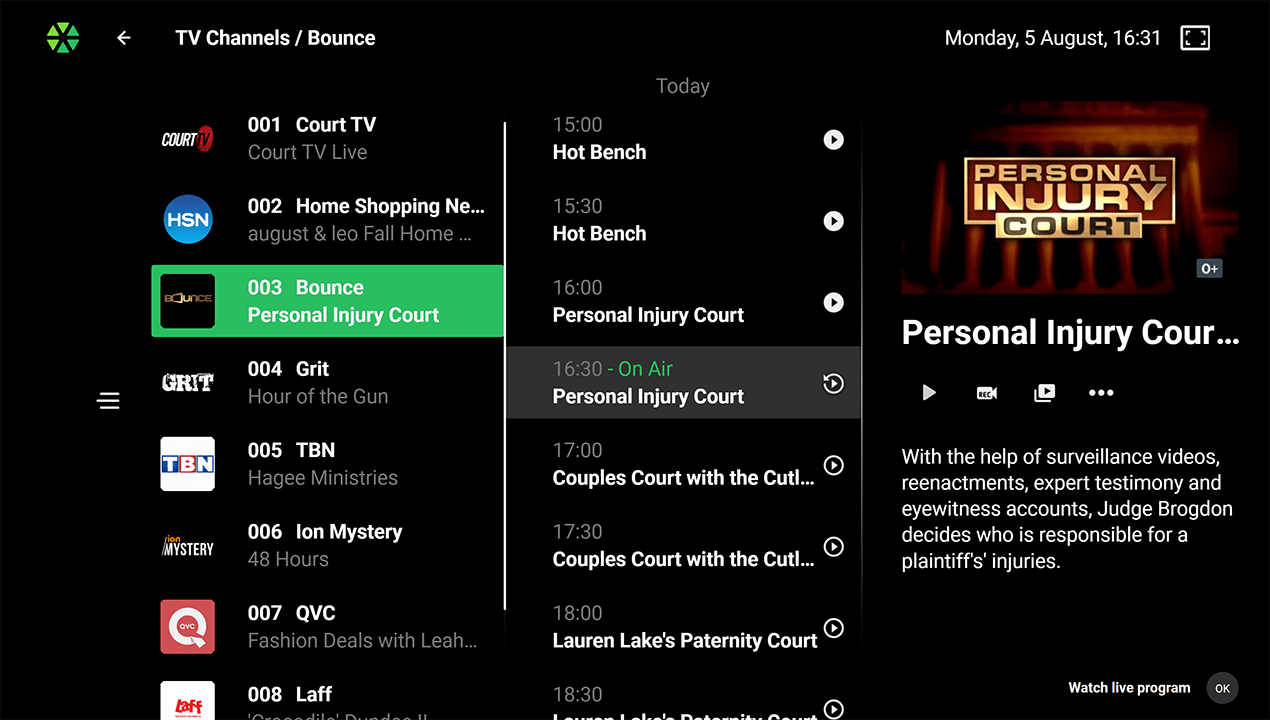 Channel List with Program Guide:
Channel List with Program Guide: Displays channels and programs in a vertical scrollable list for easy navigation. Includes detailed information about current broadcasts, channel guides, and completed/upcoming programs with description and screenshot.
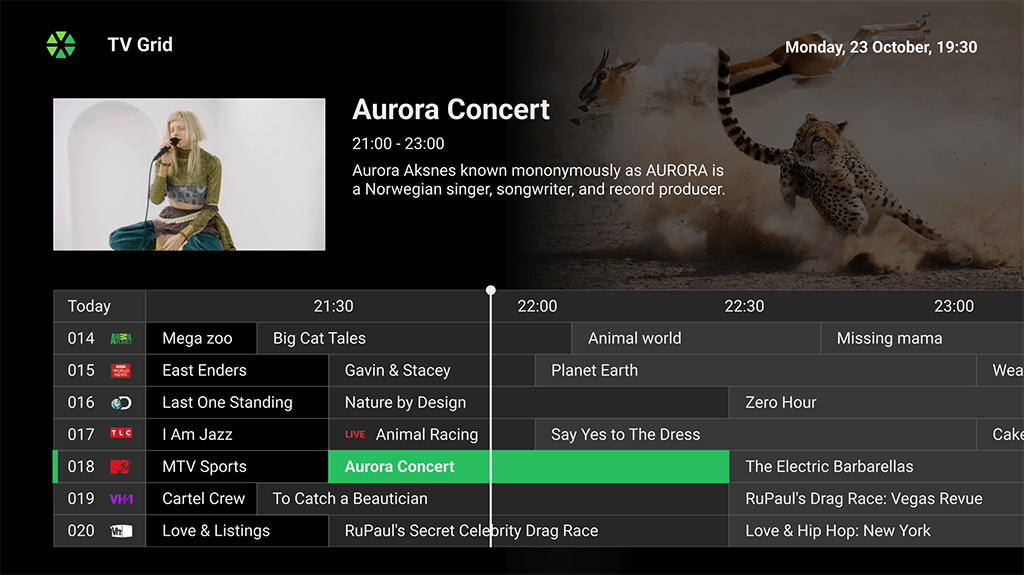 EPG Grid:
EPG Grid: A classic Electronic Program Guide available for large-screen devices. TV programs are displayed horizontally with durations on a timeline. User can select a program for more info and functions, with a window showing the current broadcast.
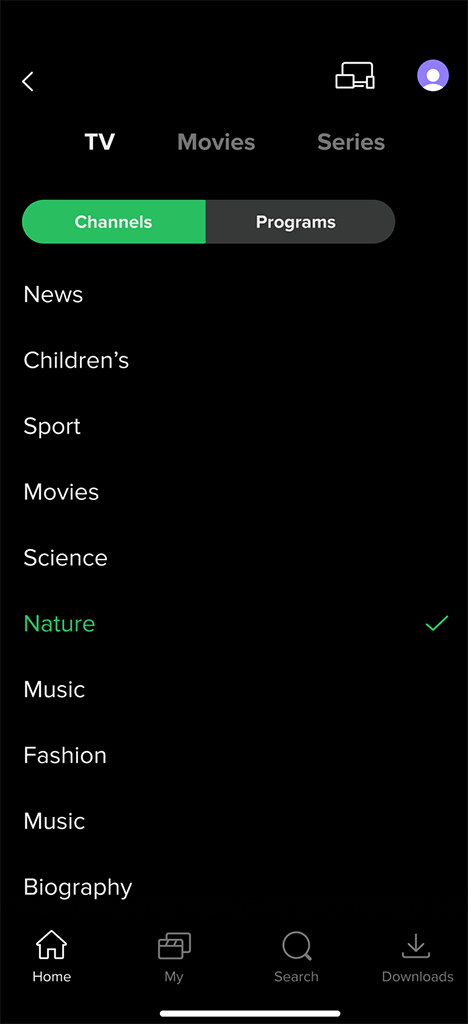
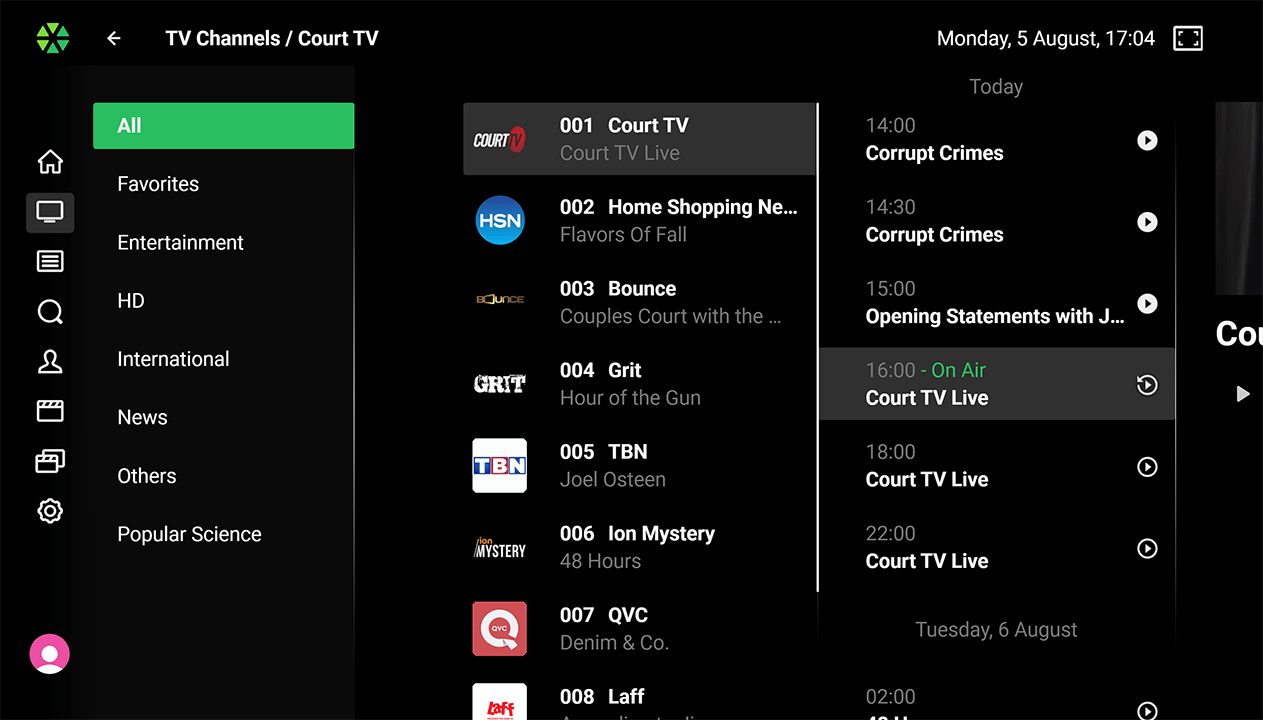 Theme-Based Channel Filtering:
Theme-Based Channel Filtering: User can filter channels by themes (such as sports, news, entertainment) or genres of currently airing programs (if the genres are provided by the EPG provider) by opening a filtering panel.
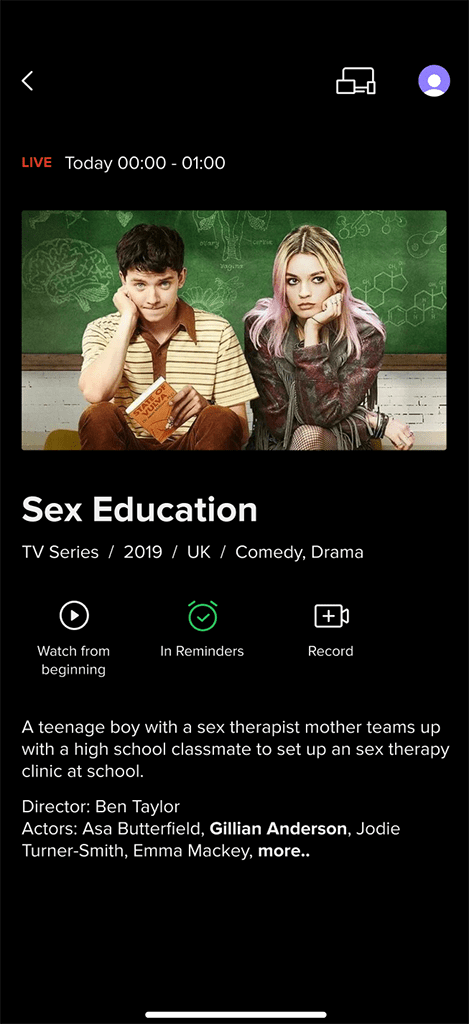
 Detailed TV Program Information:
Detailed TV Program Information: Provides in-depth details about TV programs in full-screen view, including extended description, cast, recording quota used, availability period of recorded programs, and other relevant data.
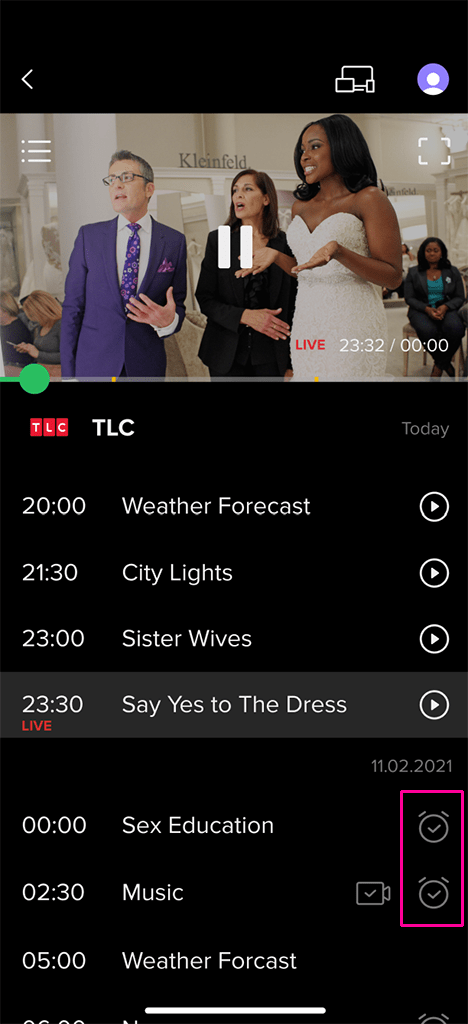
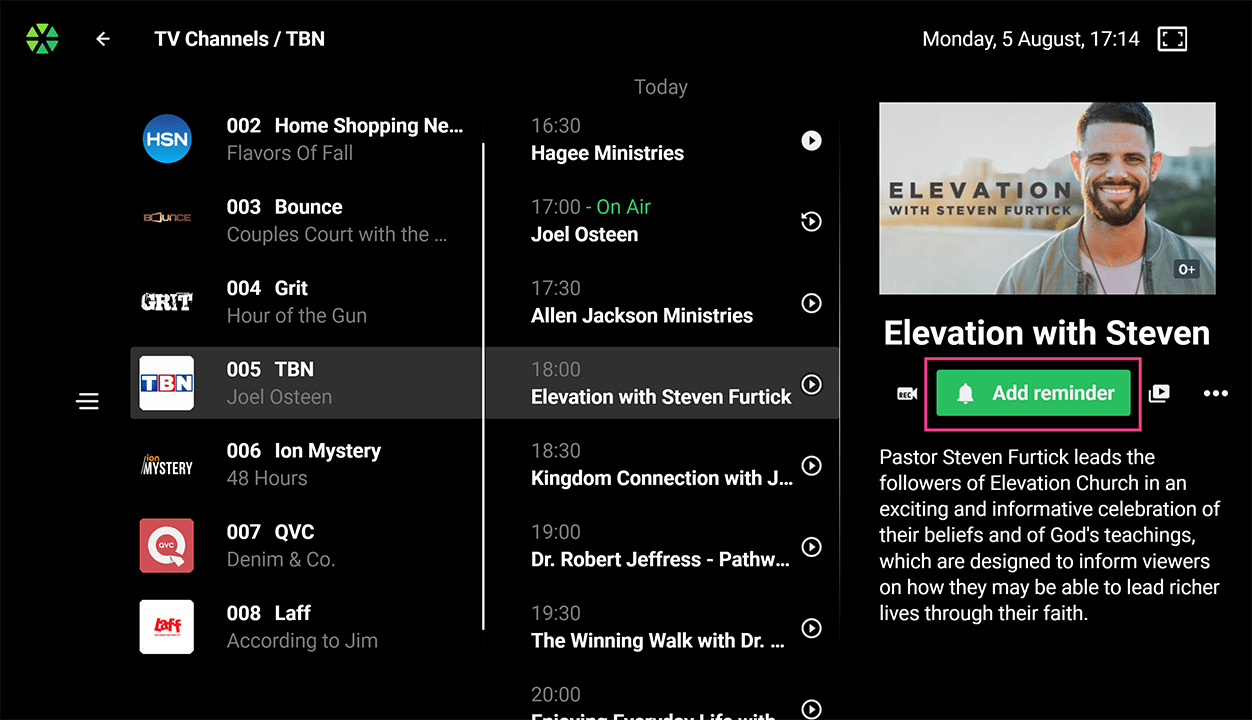 Reminders:
Reminders: Set alerts for upcoming TV programs with a pop-up before the show starts. All reminders are displayed in a dedicated menu.
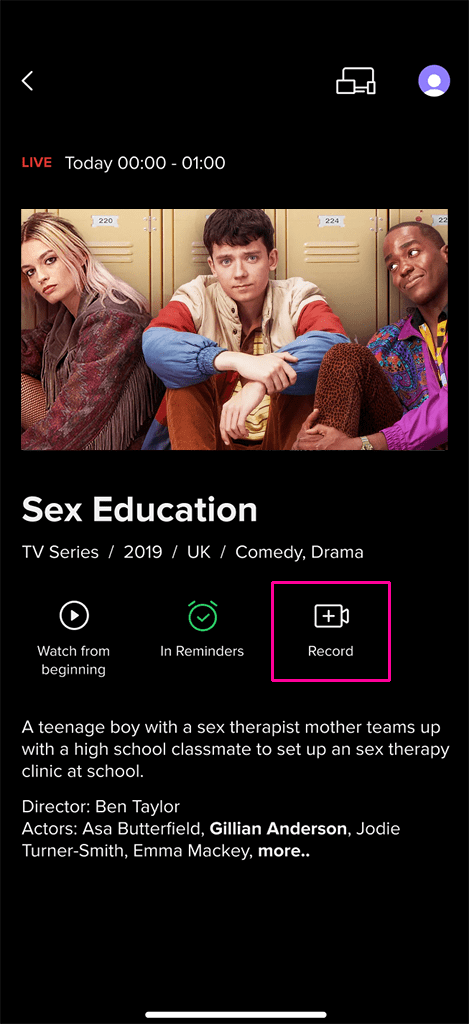
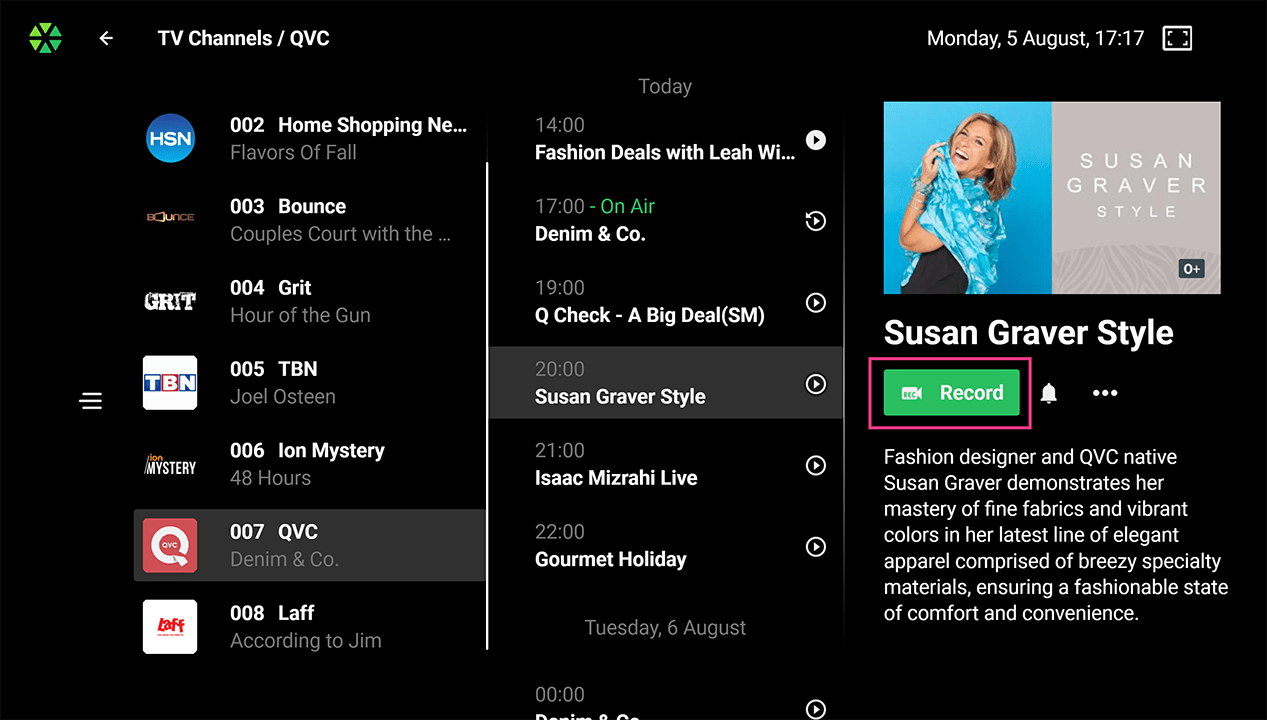 Upcoming Broadcasts Recording:
Upcoming Broadcasts Recording: This feature allows users to schedule recordings for individual programs, entire series, or based on a user-defined recurring schedule. All scheduled and completed recordings are accessible through a dedicated menu.
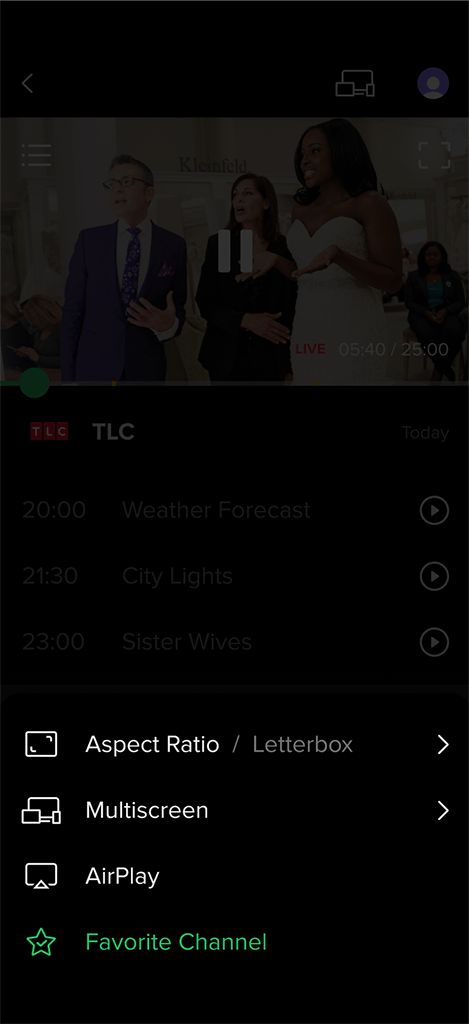
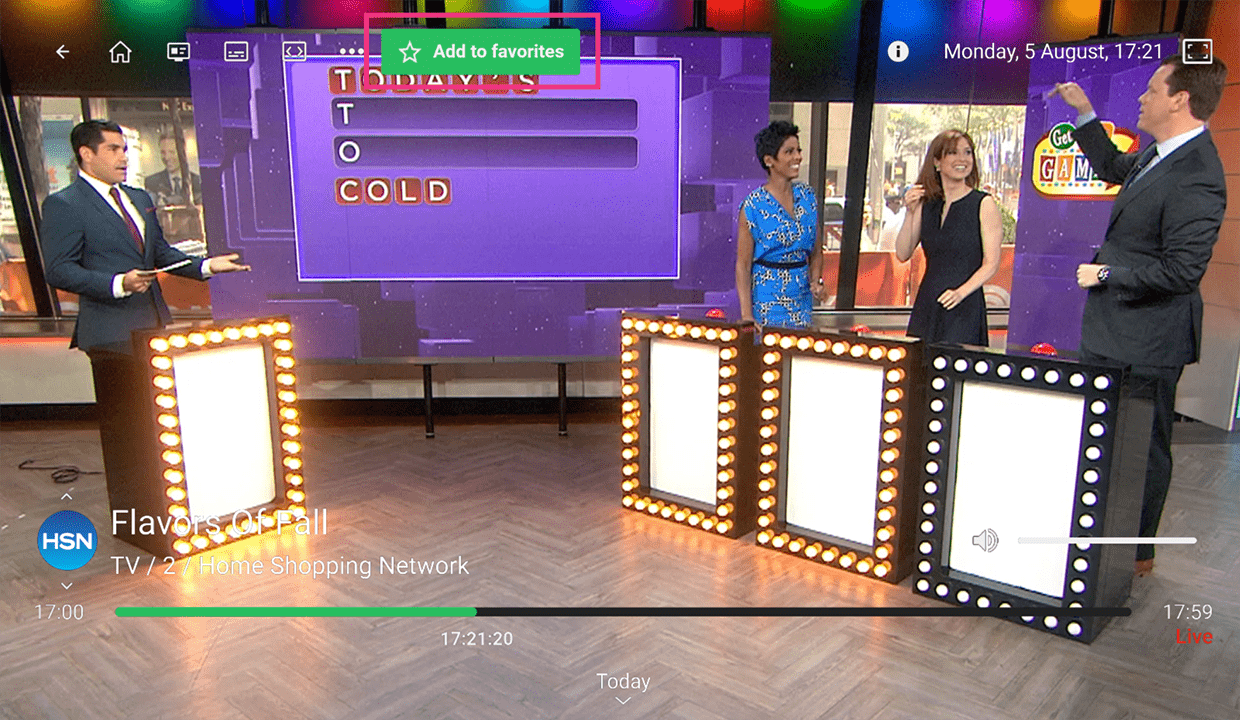
Favorite Channels: User can mark preferred channels for quick access. The favorite channels appear first on the Home screen and in the channel filtering section.
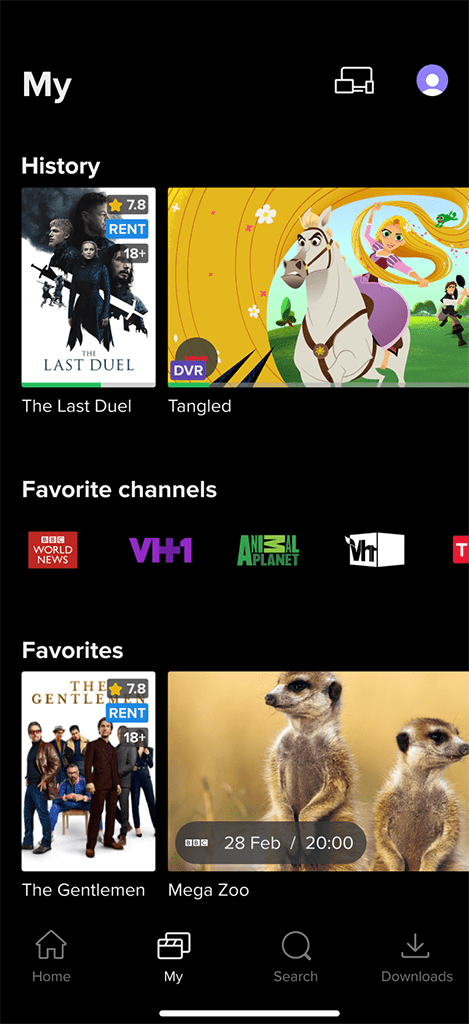
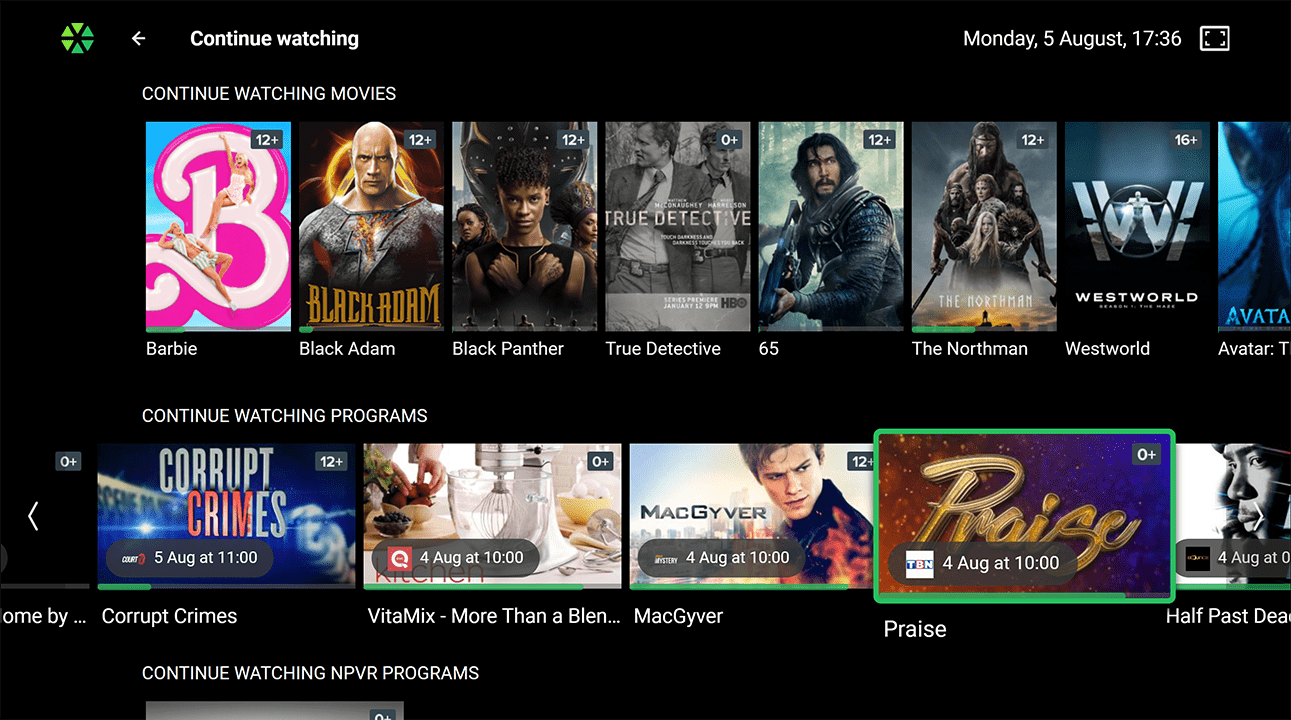 Watch History:
Watch History: The list of recently viewed programs, with the option to resume from where the user left off. Users can also choose to clear their entire watch history or remove individual items.
The full-screen player in SmartTUBE Apps for large-screen devices supports the following features:
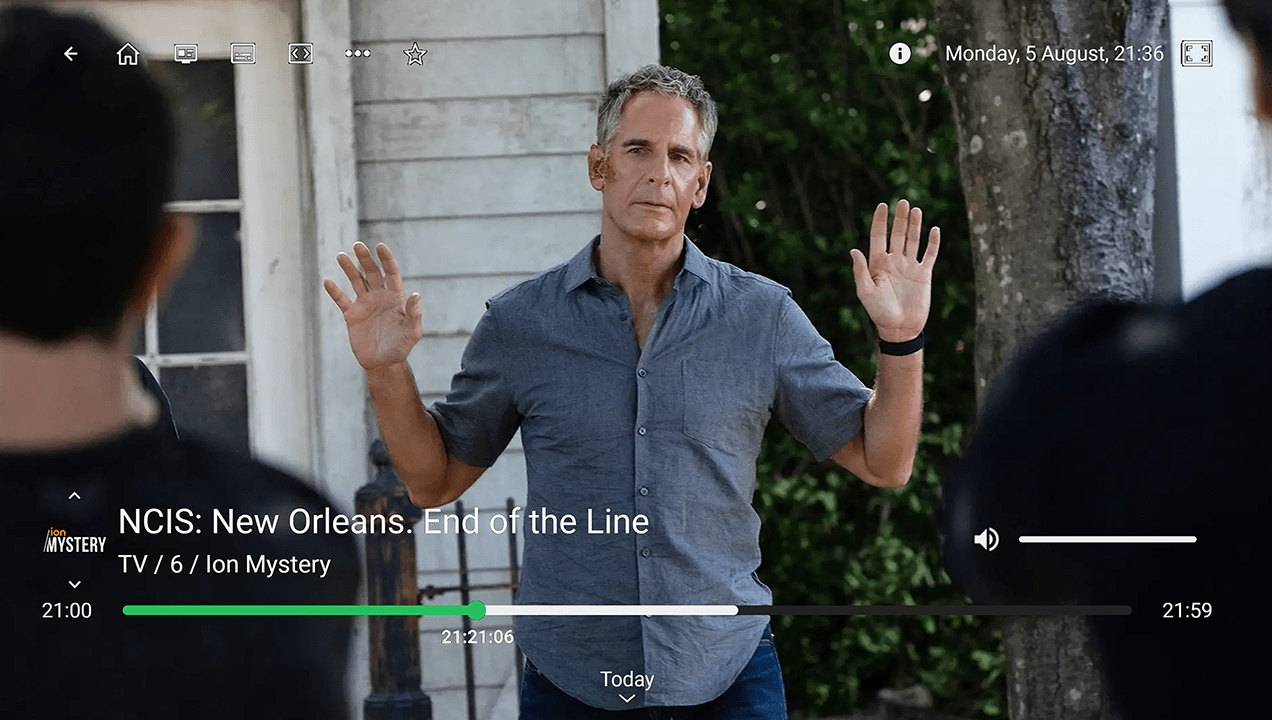
Playing live streams and rewinding, fast forwarding, and pausing catch-up content.
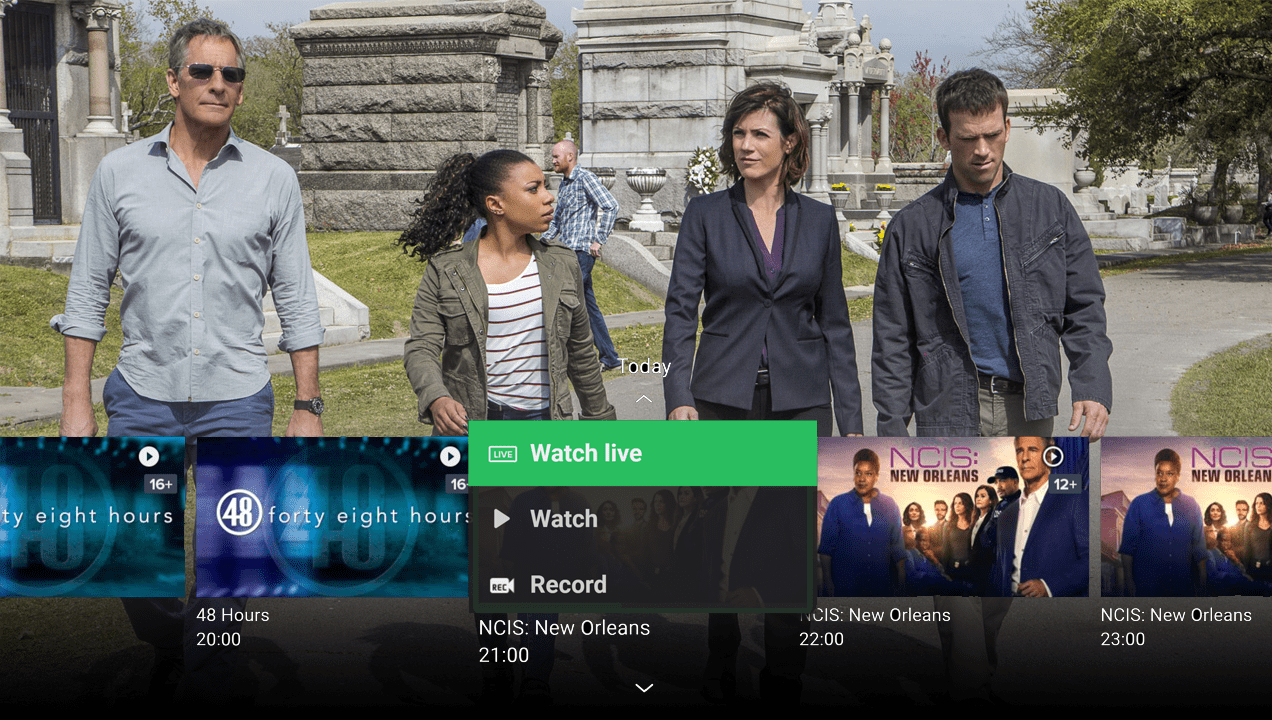
Revealing the program guide rail for the current channel, enabling setting reminders or recordings for upcoming programs. Available for the large-screen apps only.

Adjusting the stream’s aspect ratio, selecting the audio/video/subtitle track, viewing the program details, and checking the stream technical information.
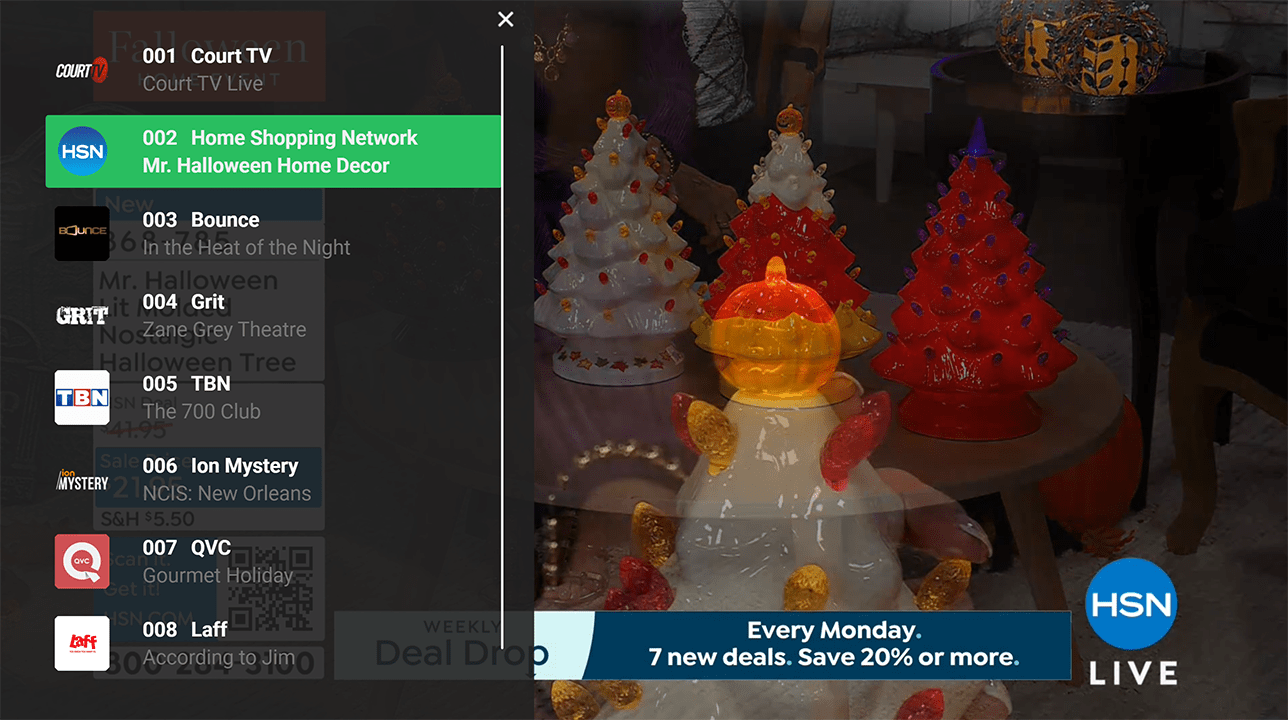
Quick channel selection panel allowing to switch channels visually without leaving full screen mode.
The full-screen player in SmartTUBE Apps for mobile iOS / Android devices supports the following features:

Playing live streams and rewinding, fast forwarding, pausing catch-up content, as well as selecting audio/video/subtitle tracks.
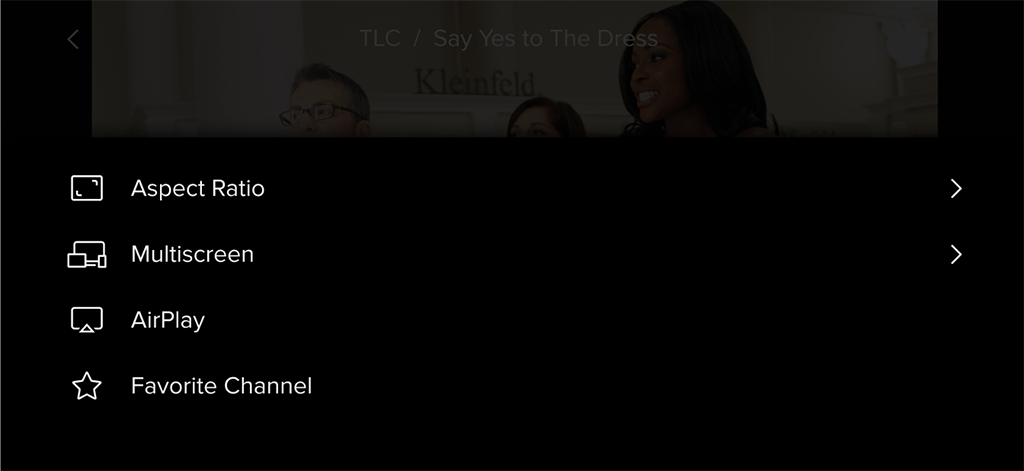
Adjusting the stream’s aspect ratio, sharing the stream across other subscribers’ devices, and exploring additional functions.
The full-screen player in SmartTUBE Apps for mobile iOS / Android devices can be controlled by tapping, swiping, and sliding:
- Short tap: Opens playback controls and settings menu, which disappear after 3 seconds of no user activity.
- Double tap in the center: Switches between full-screen and portrait mode.
- Double tap on the left/right area: Rewinds backward/forward for 10 seconds.
- Swipe left/right: Switches channels.
- Slide by the left/right area: Controls the brightness and volume, respectively:
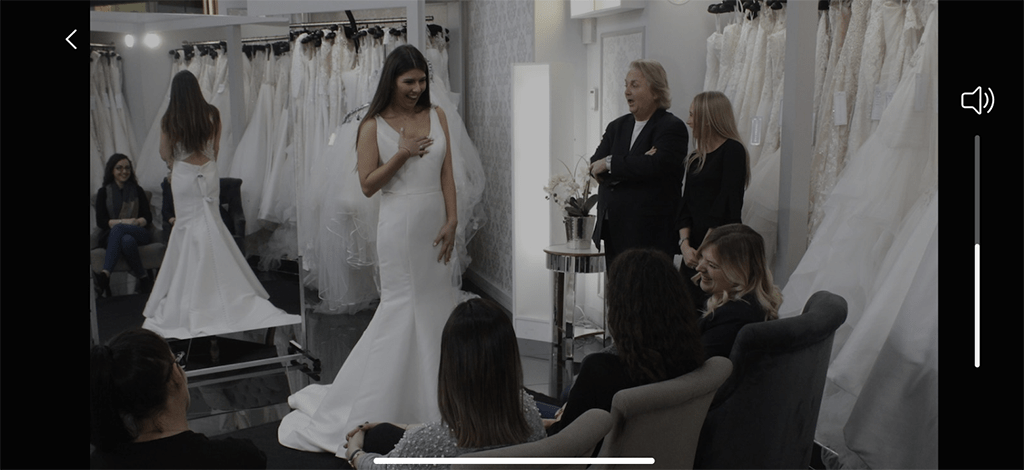


VoD Content
SmartTUBE Apps offer fast navigation and search within the VoD content library, payment options, a recommendation tool that suggests relevant content based on subscriber preferences, and other helpful features:
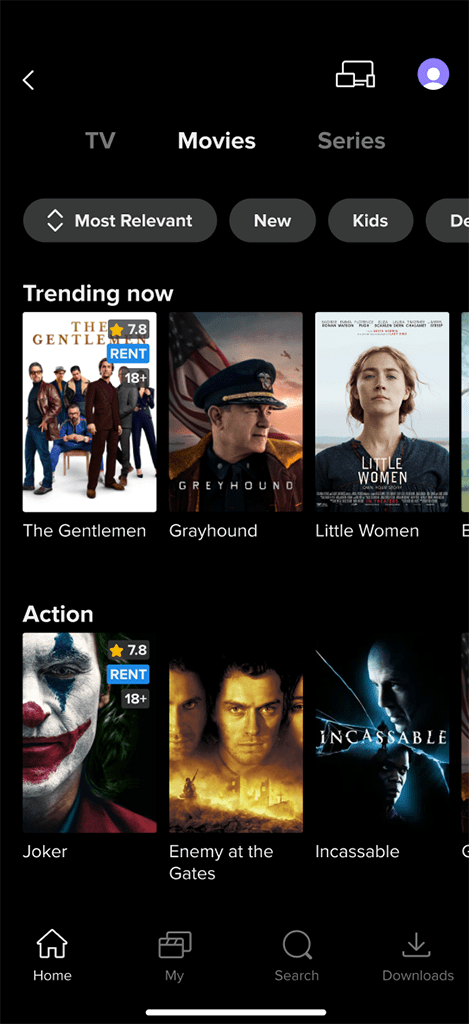
 VoD Content Catalog:
VoD Content Catalog: Displays available content with posters and titles in a mosaic view or as a list of themed rails.
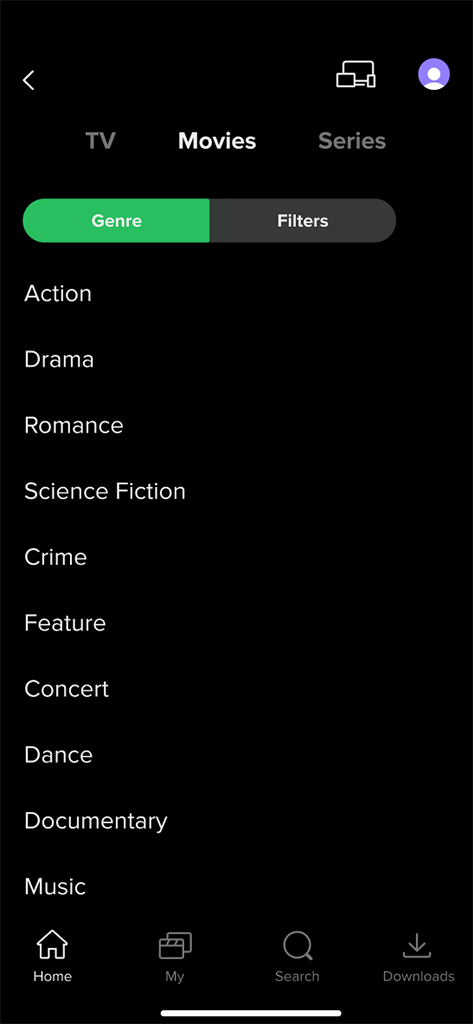
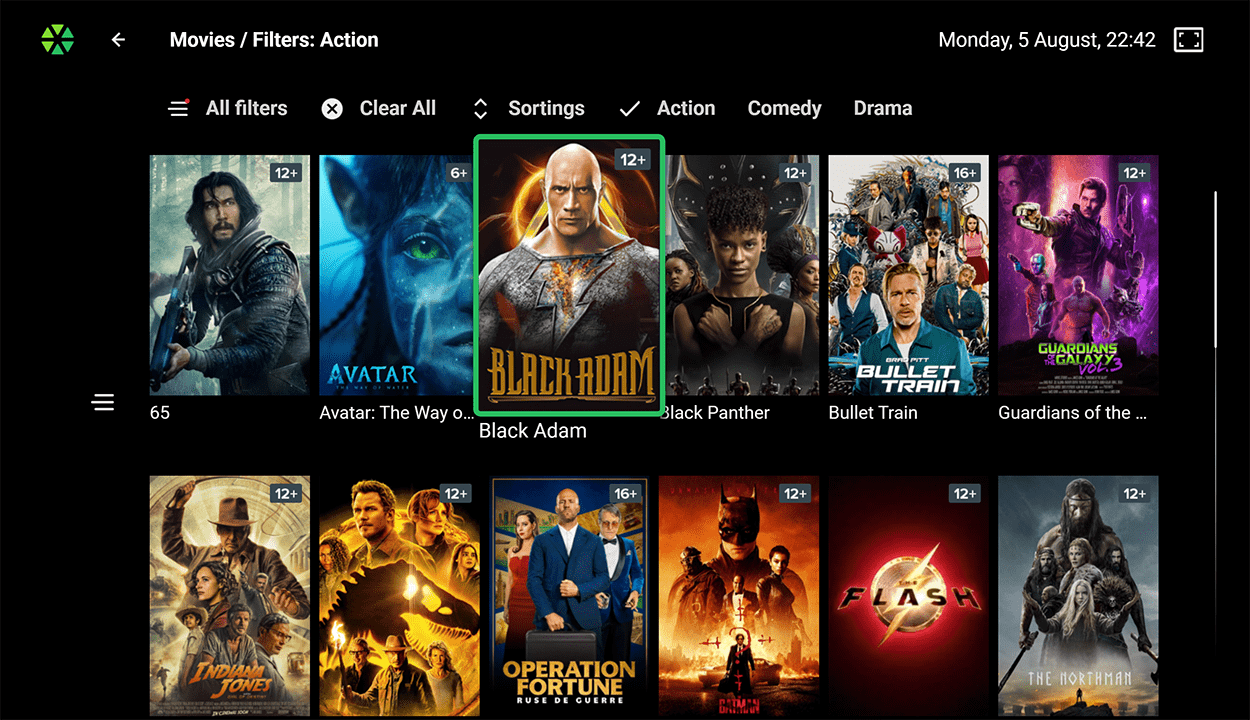
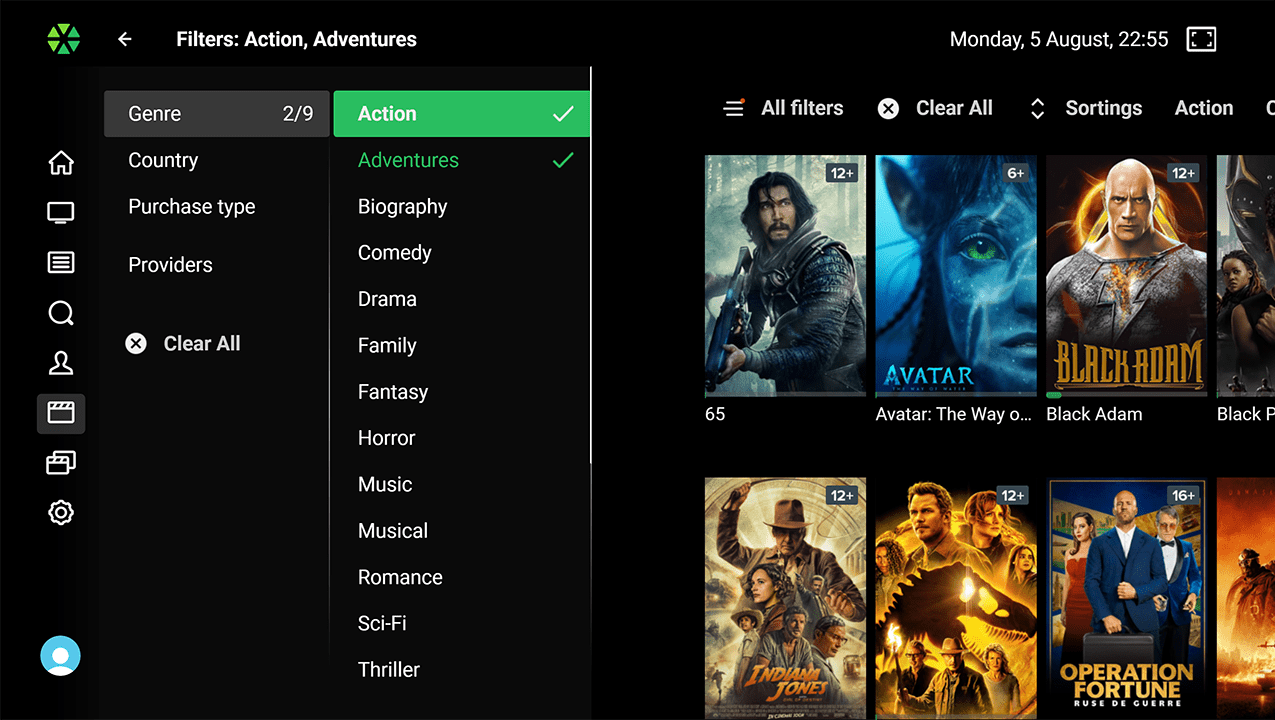 Content Filtering:
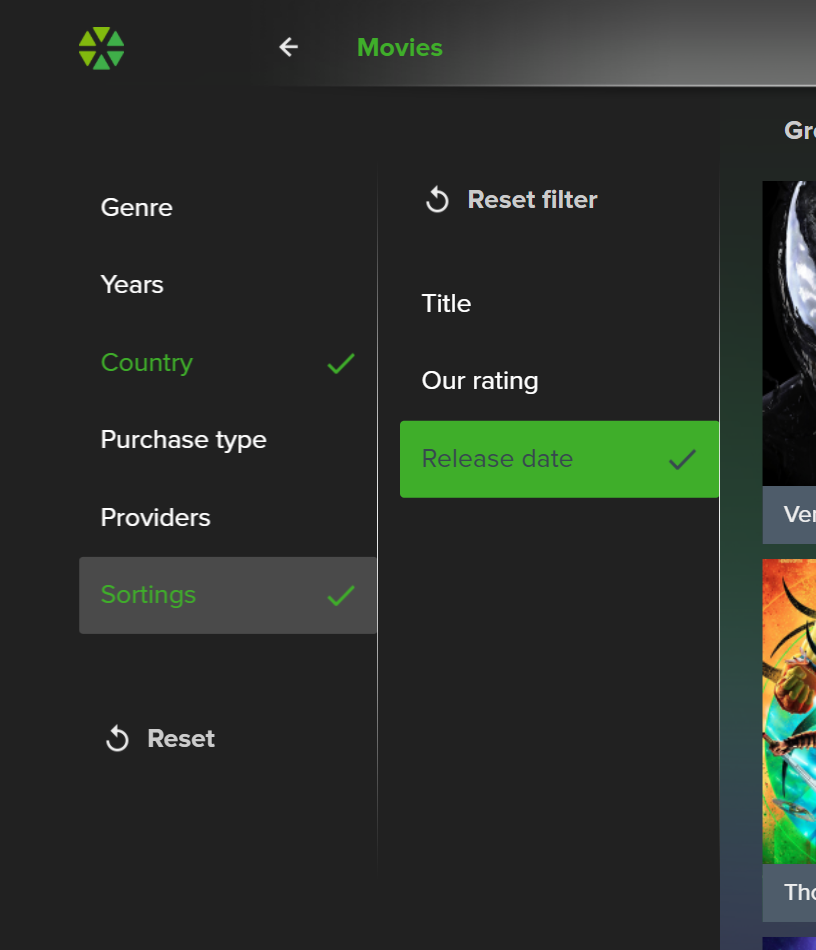
Content Filtering: Users can filter content by type (movies, series, for kids), genre (adventure, comedy, detectives, etc.), production year, country, and other criteria.
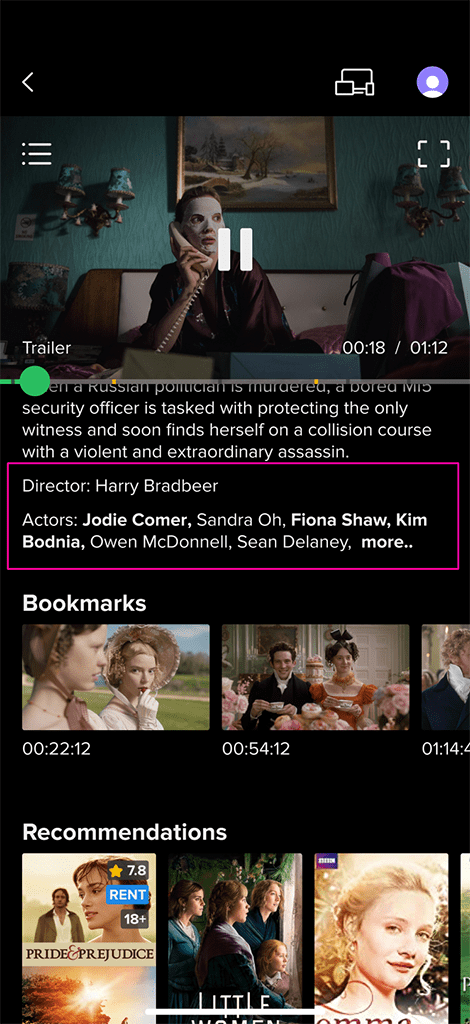
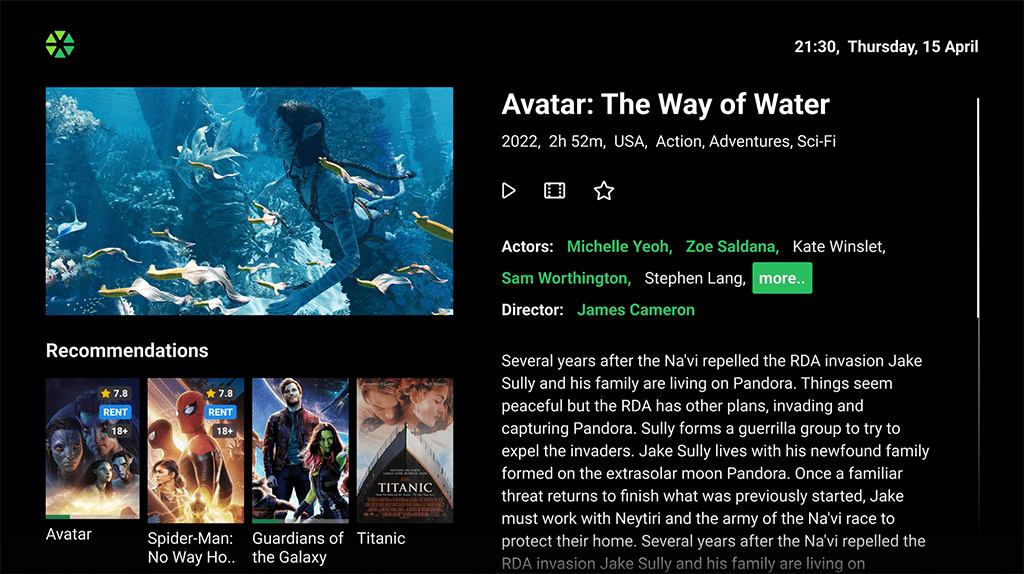 Detailed Content Description:
Detailed Content Description: Provides information on the movie description, directors, actors, ratings, age restrictions, release year, screenshots, etc. for selected content.
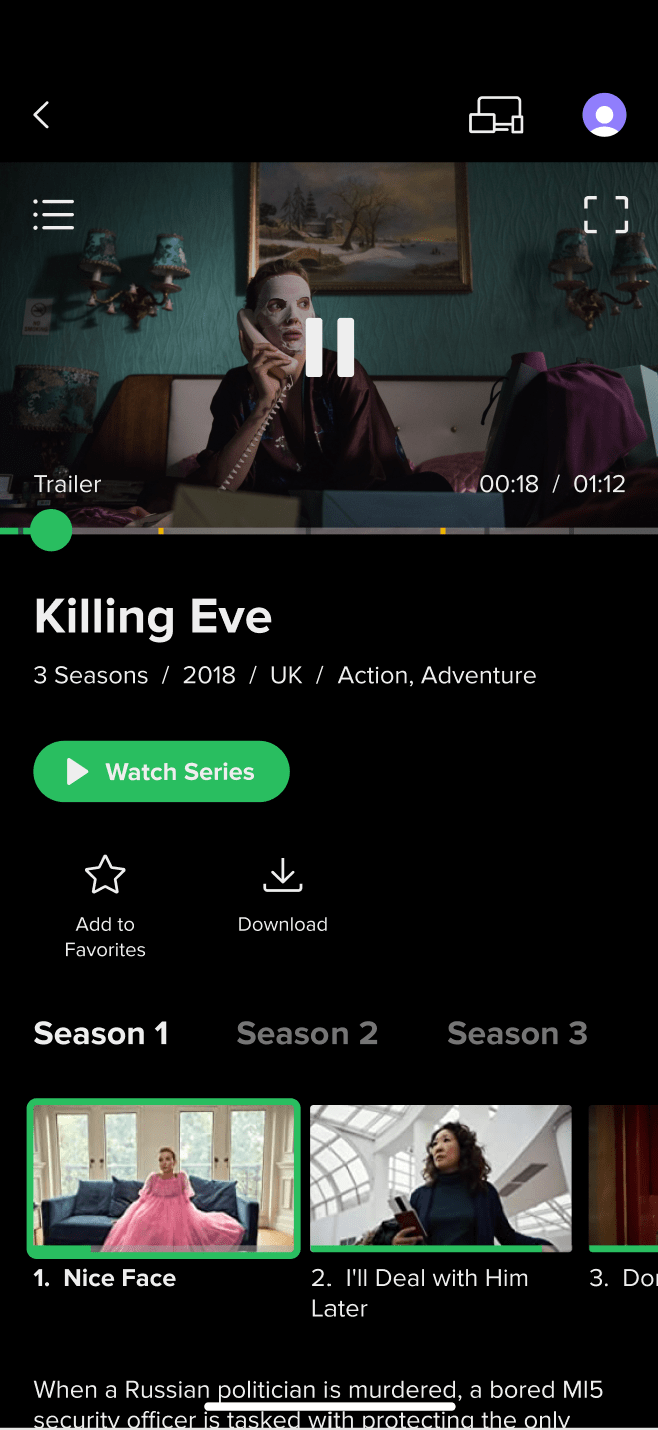
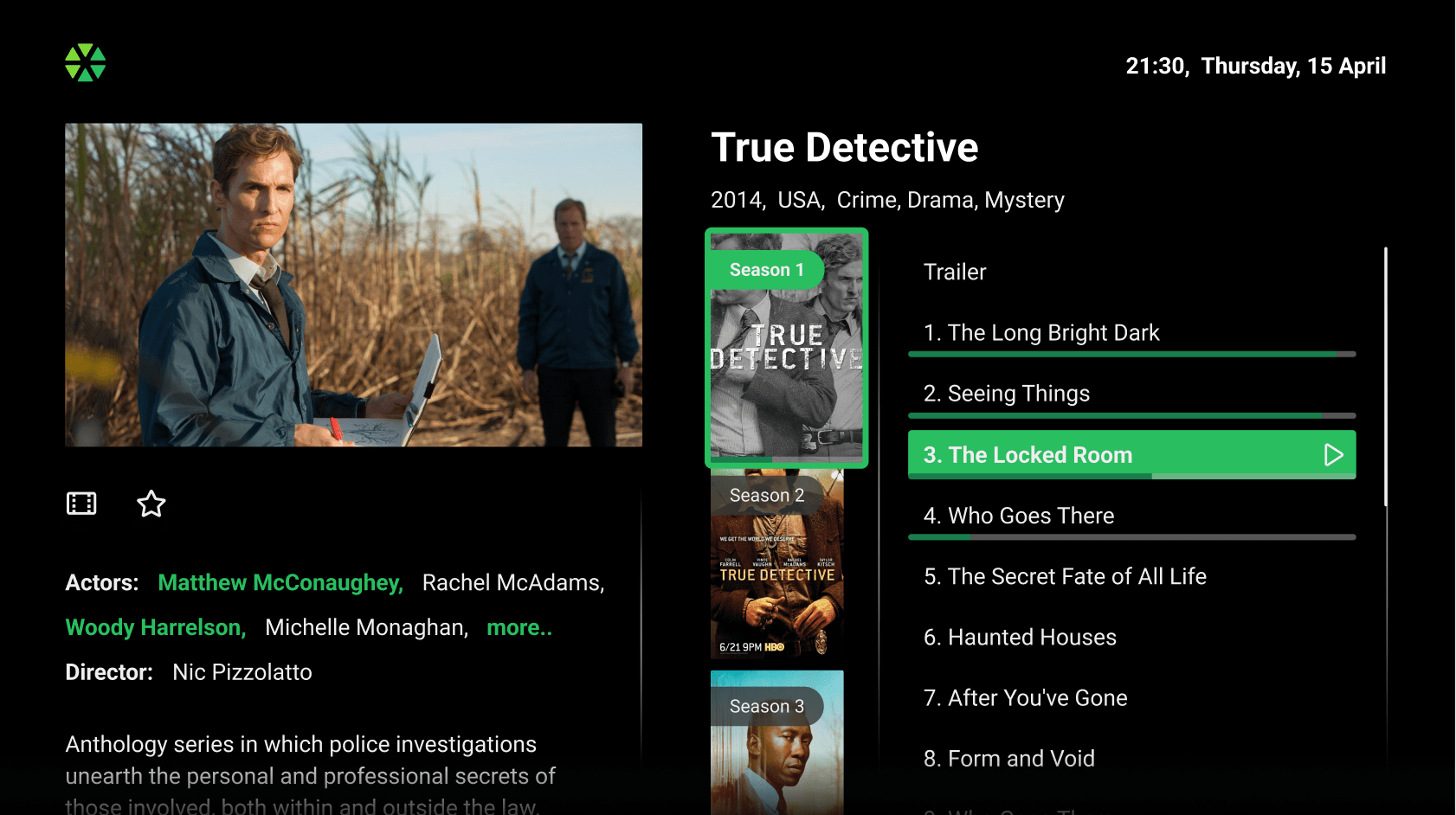 Detailed Series Description:
Detailed Series Description: In addition to the information described above, this feature offers a convenient way to select from the various seasons and episodes of a series.
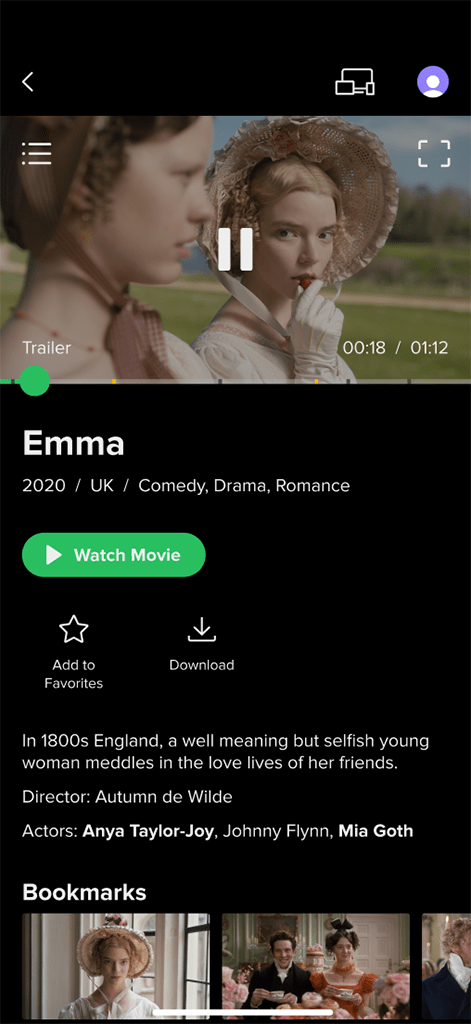
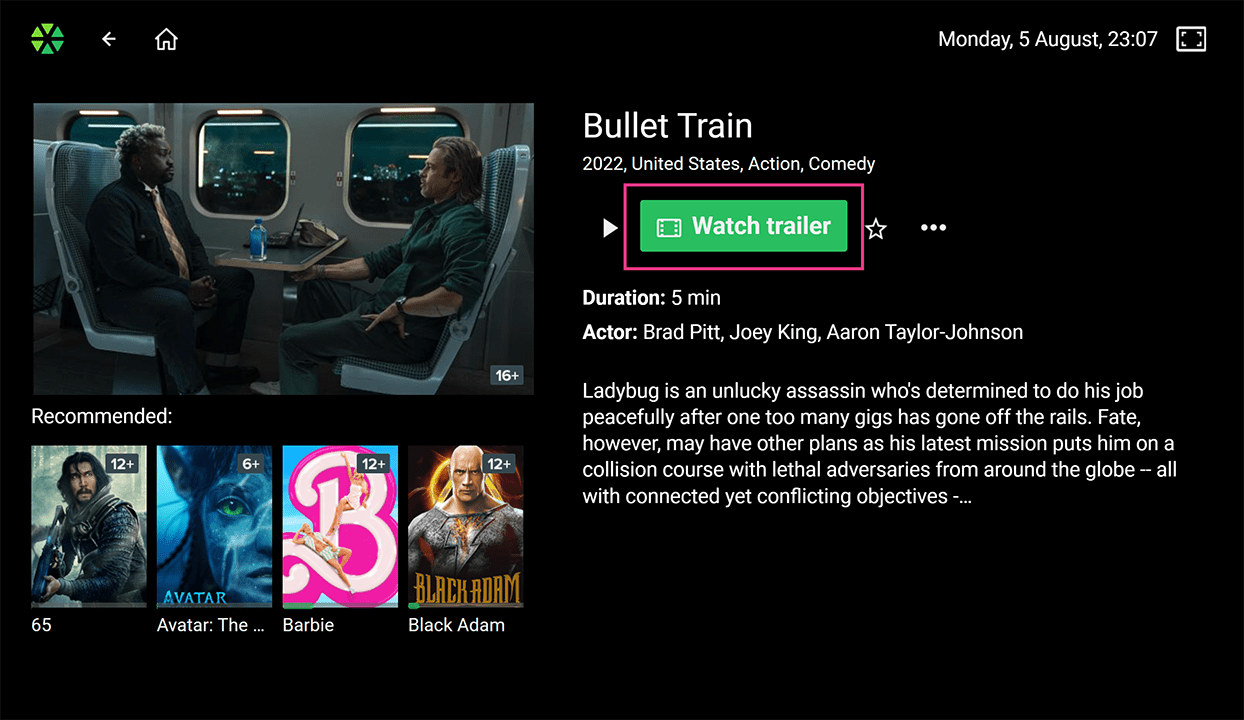 Trailer Viewing:
Trailer Viewing: Users can watch trailers within the movie card if available.
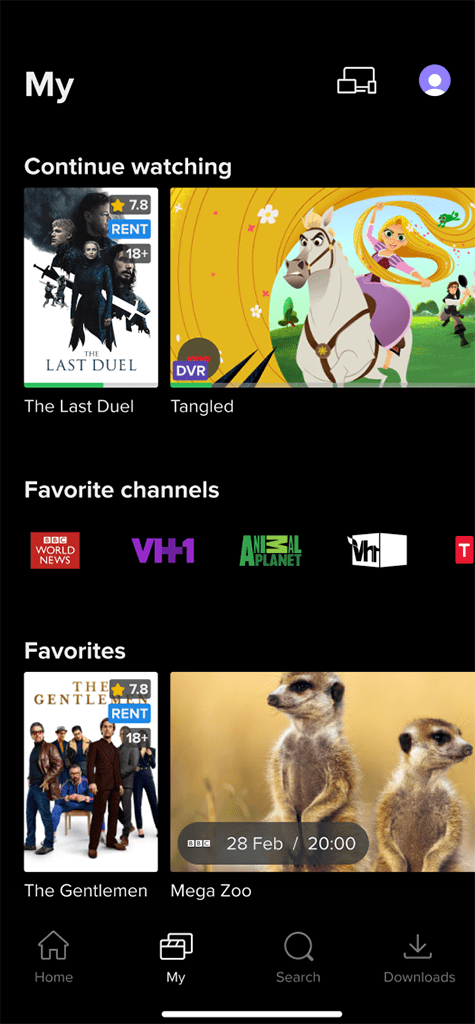
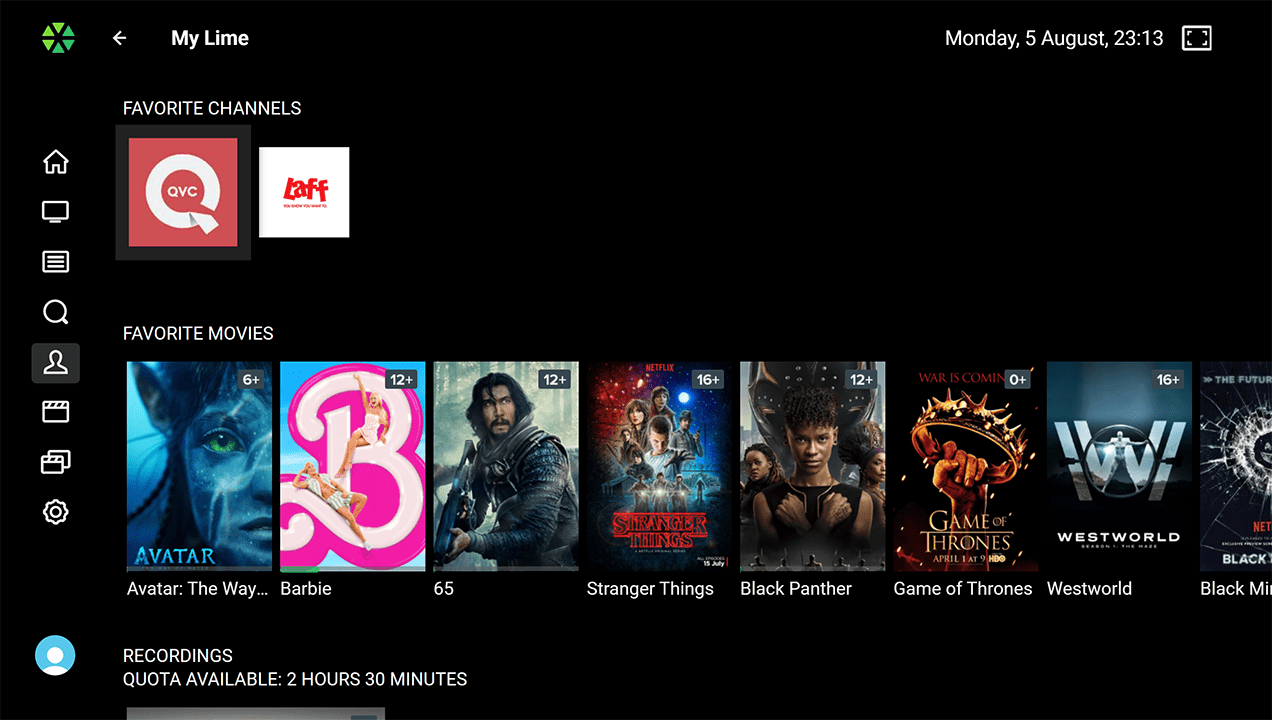 List of Favorites:
List of Favorites: Allows users to save their preferred movies for convenient access and later viewing.
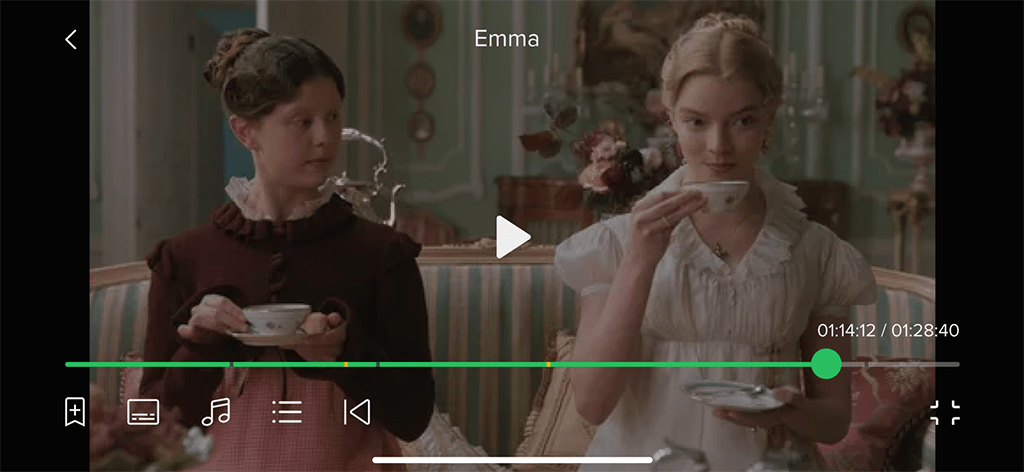
 Full-Screen Player:
Full-Screen Player: Content is played in full-screen mode with playback controls, video quality and aspect ratio options, audio track and subtitle selection, content recommendations (in the large-screen apps), adding to favorites, and technical information about the stream (in the large-screen apps).
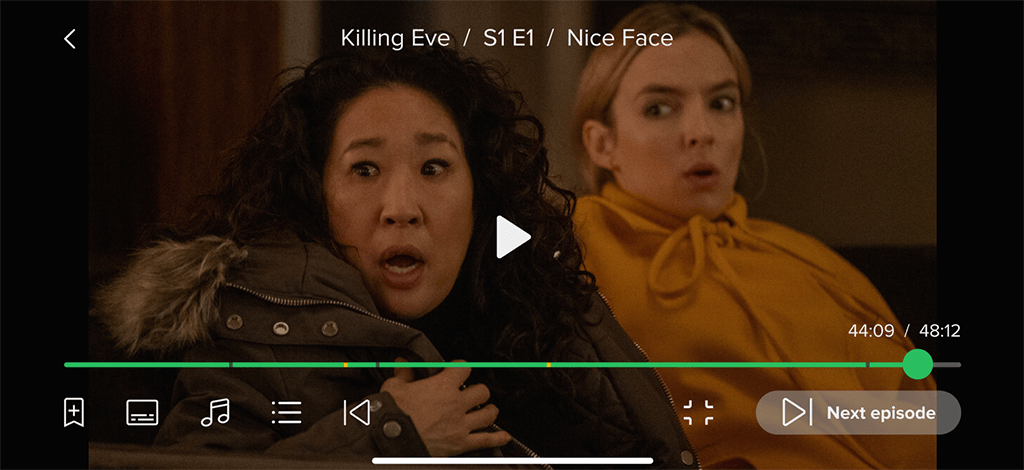
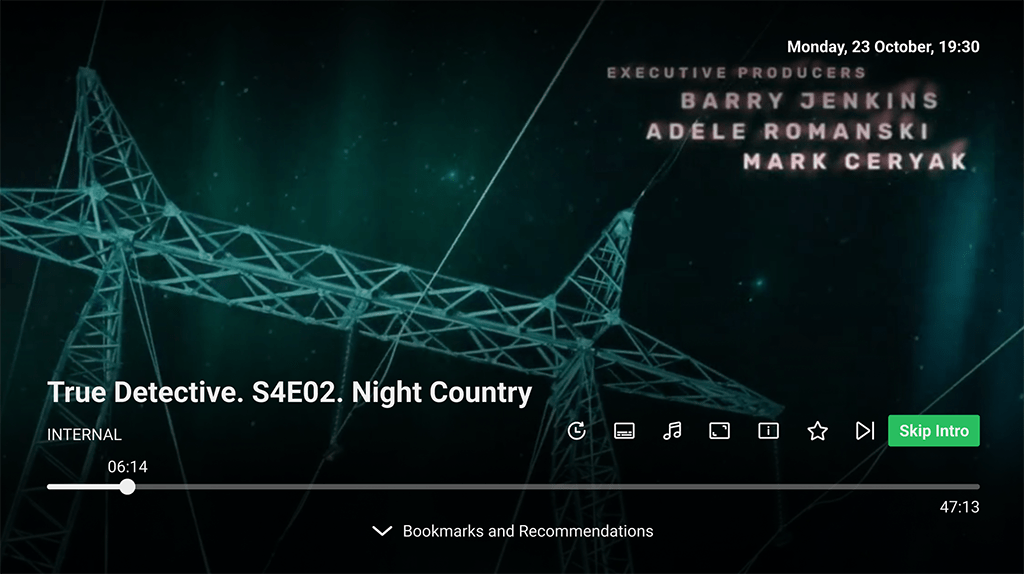
Skip Opening and Credits: The full-screen player allows users to skip the movie’s opening credits and jump straight into the action. At the end of a series episode, users can bypass the final credits and start the next episode immediately. This feature includes a timer for auto-skipping the opening and automatically starting the next episode, with progress displayed on the button.
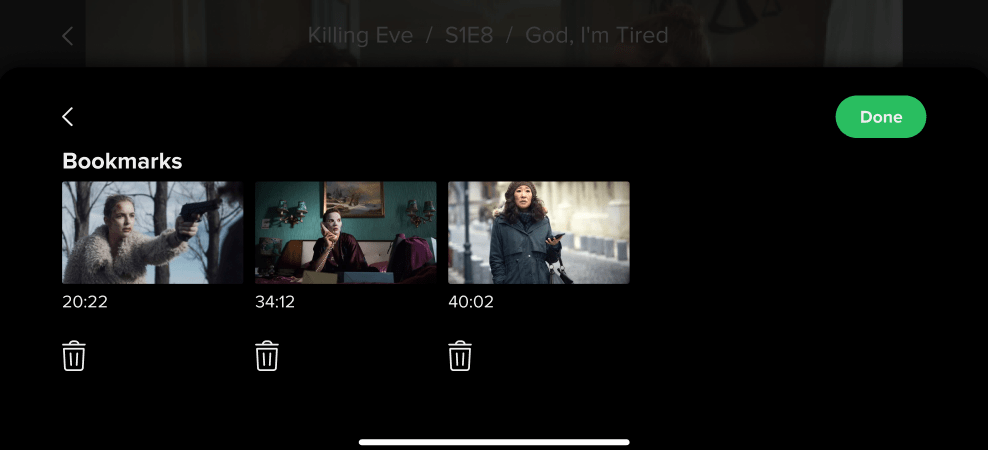
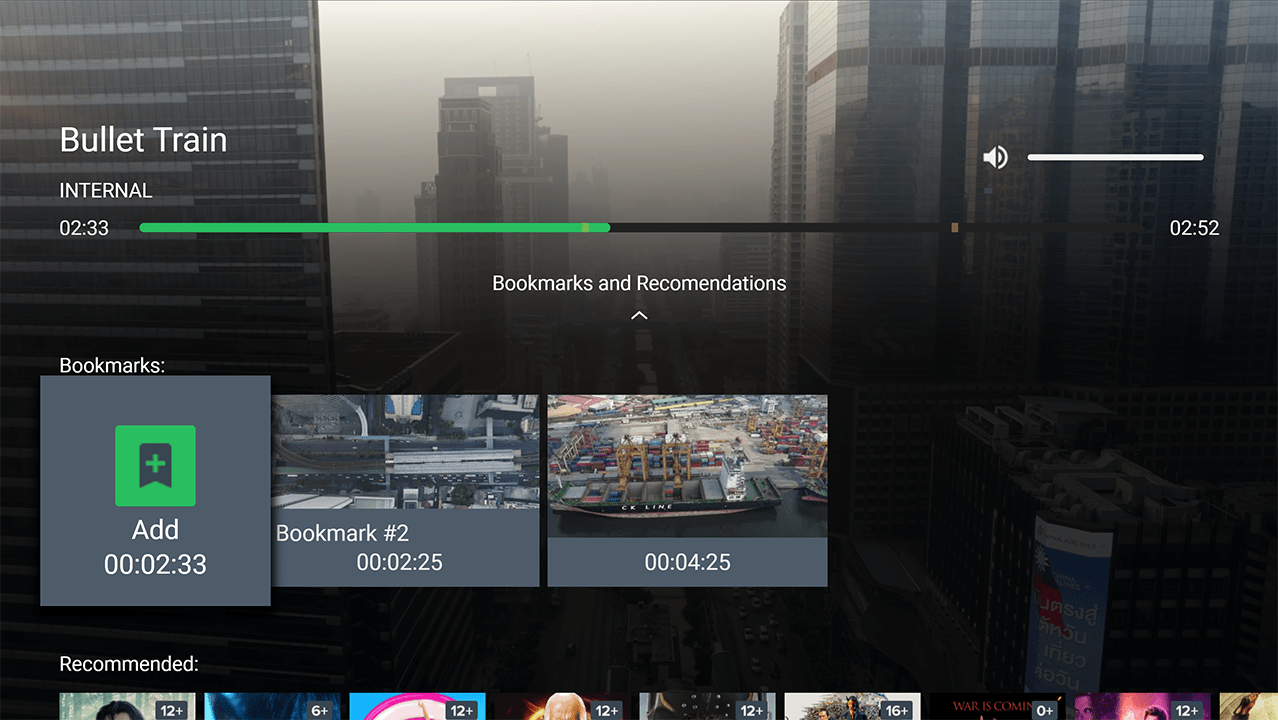 Content Bookmarks:
Content Bookmarks: Users can add bookmarks to specific movie moments. A single movie can have multiple bookmarks.
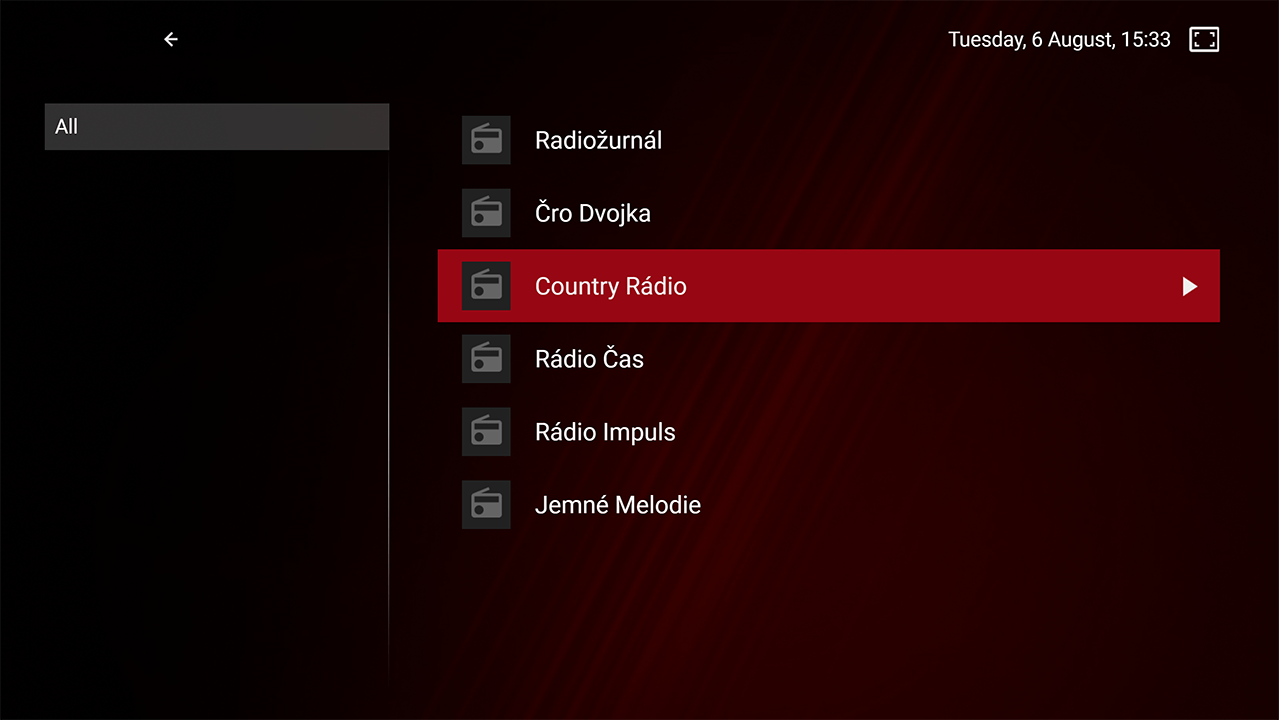
Radio Stations
SmartTUBE Apps for STB and Smart TV support the radio station broadcasting:
Media Player
The Media player integrated into SmartTUBE Apps offers all the essential features for a seamless and enjoyable content-watching experience. It may support different audio/video codecs and streaming protocols, such as MPEG-DASH and/or HLS, depending on the device.
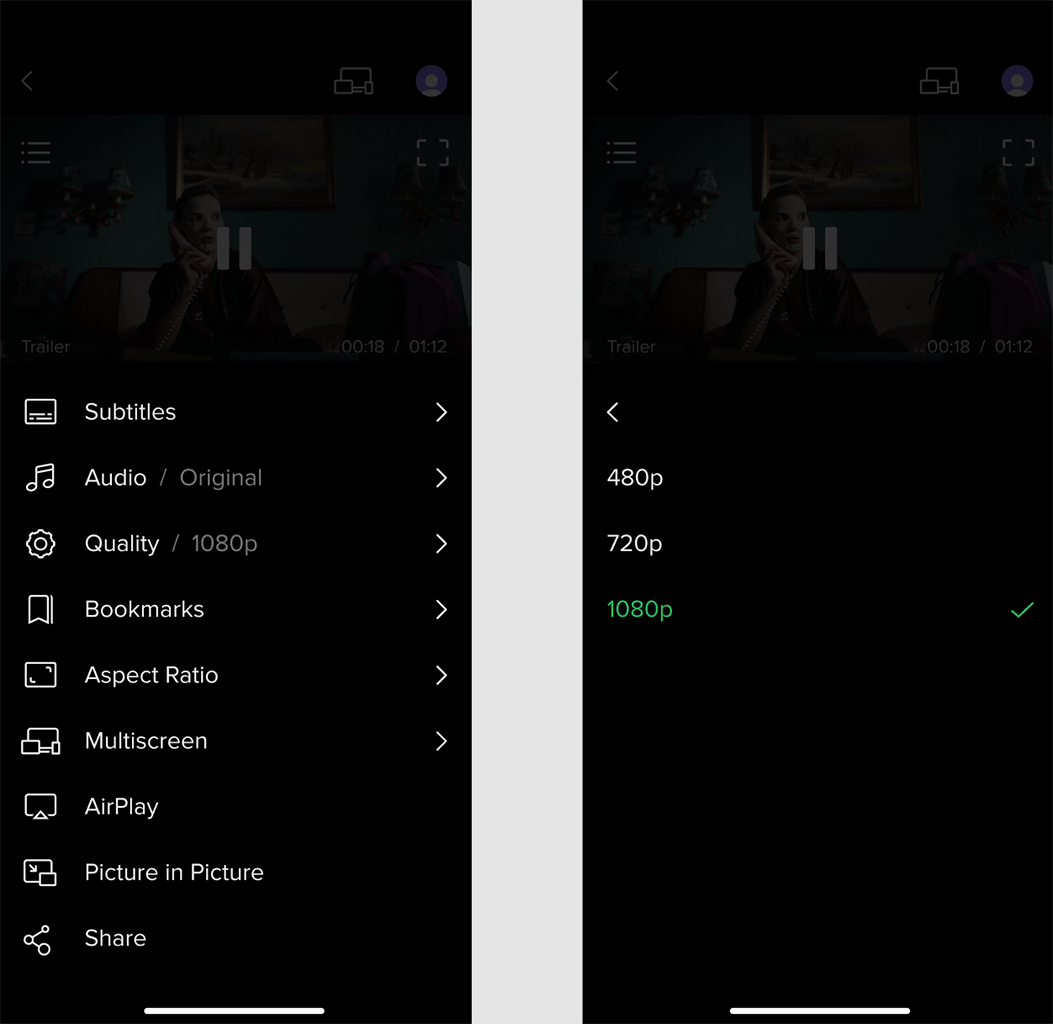
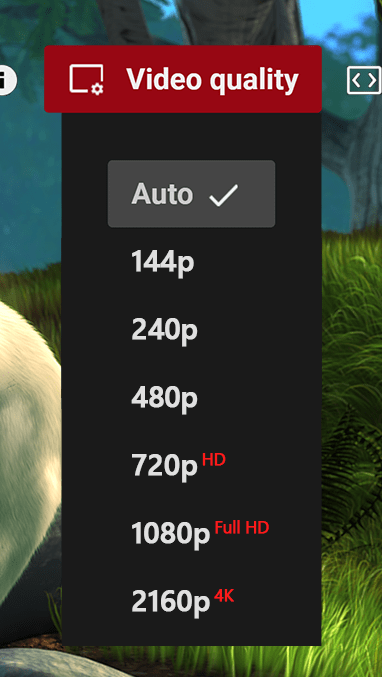 Adaptive Streaming Support:
Adaptive Streaming Support: Automatically switches between bitrates within the media stream based on network bandwidth. This prevents playback from stopping when bandwidth decreases; instead, it shifts to a lower quality stream. When bandwidth improves, video quality is restored.
Stream Quality Options: In addition to automatic adaptive switching between stream bitrates, users can also manually select their preferred stream quality.
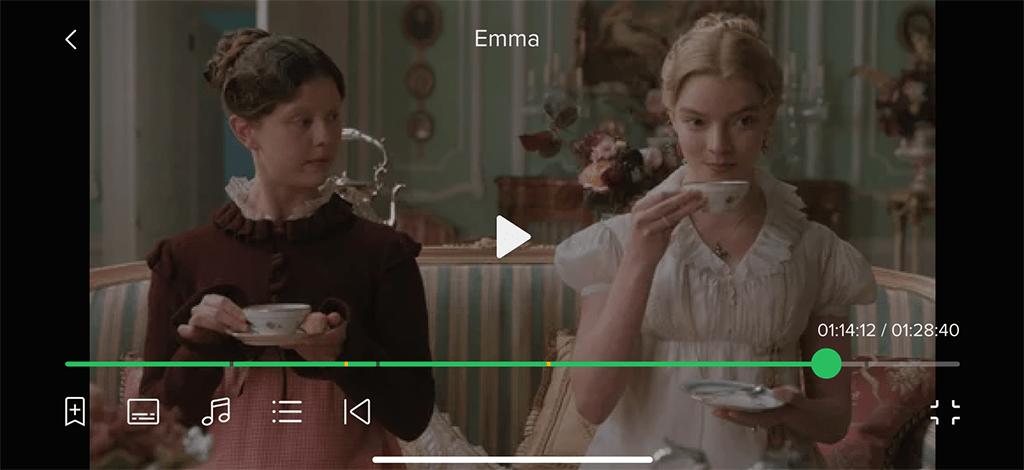
 Playback Control:
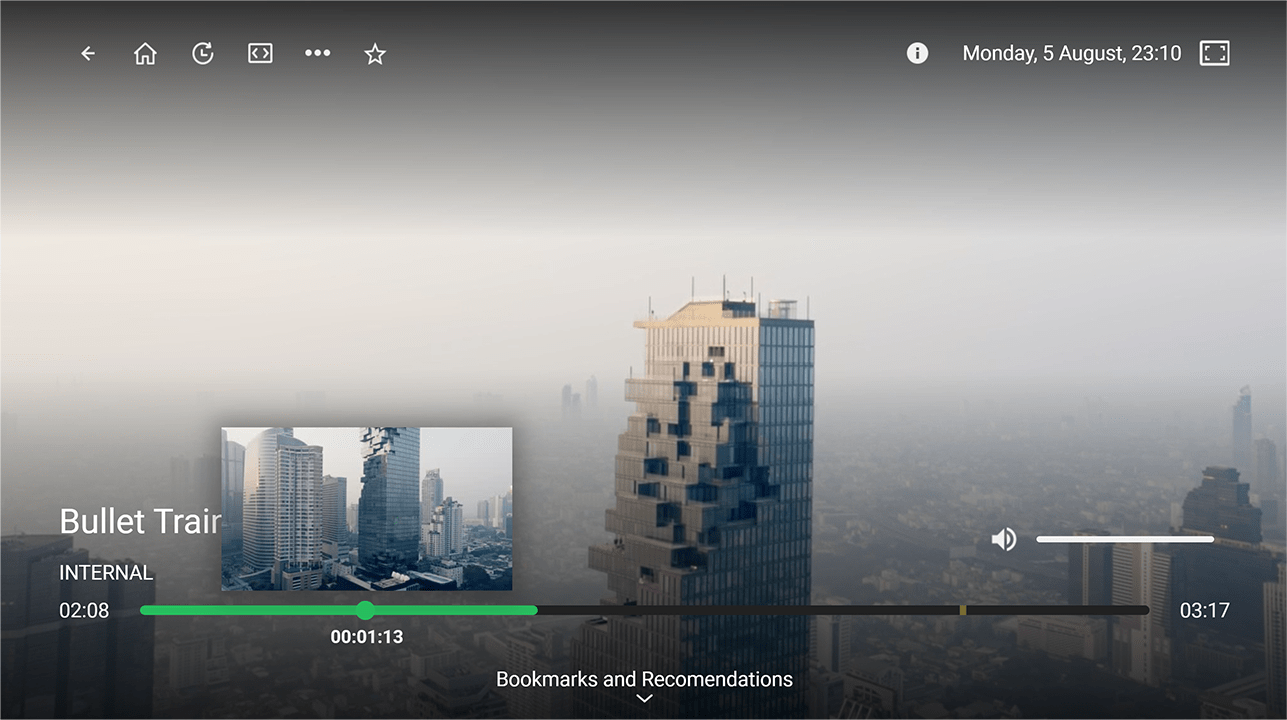
Playback Control: Lets users rewind, fast forward, and pause catch-up and xVoD content. When a video is rewound or paused, thumbnails appear above the progress bar.
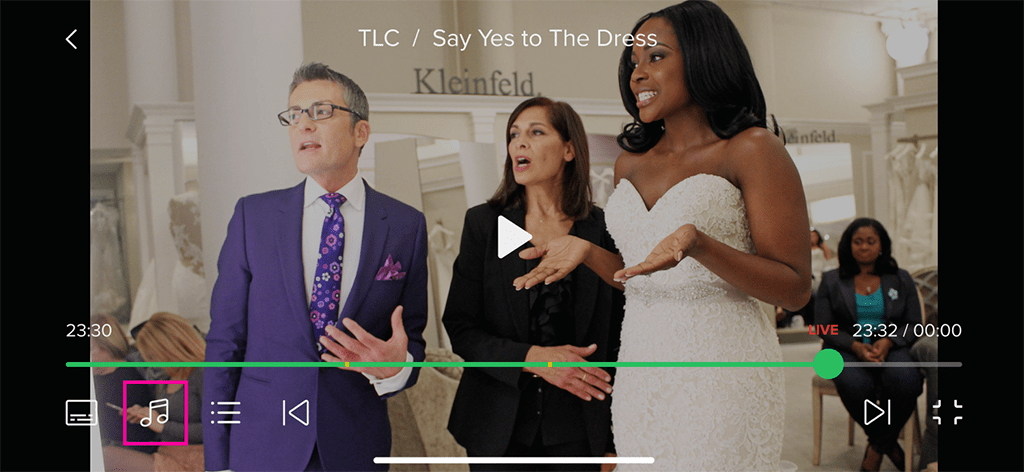
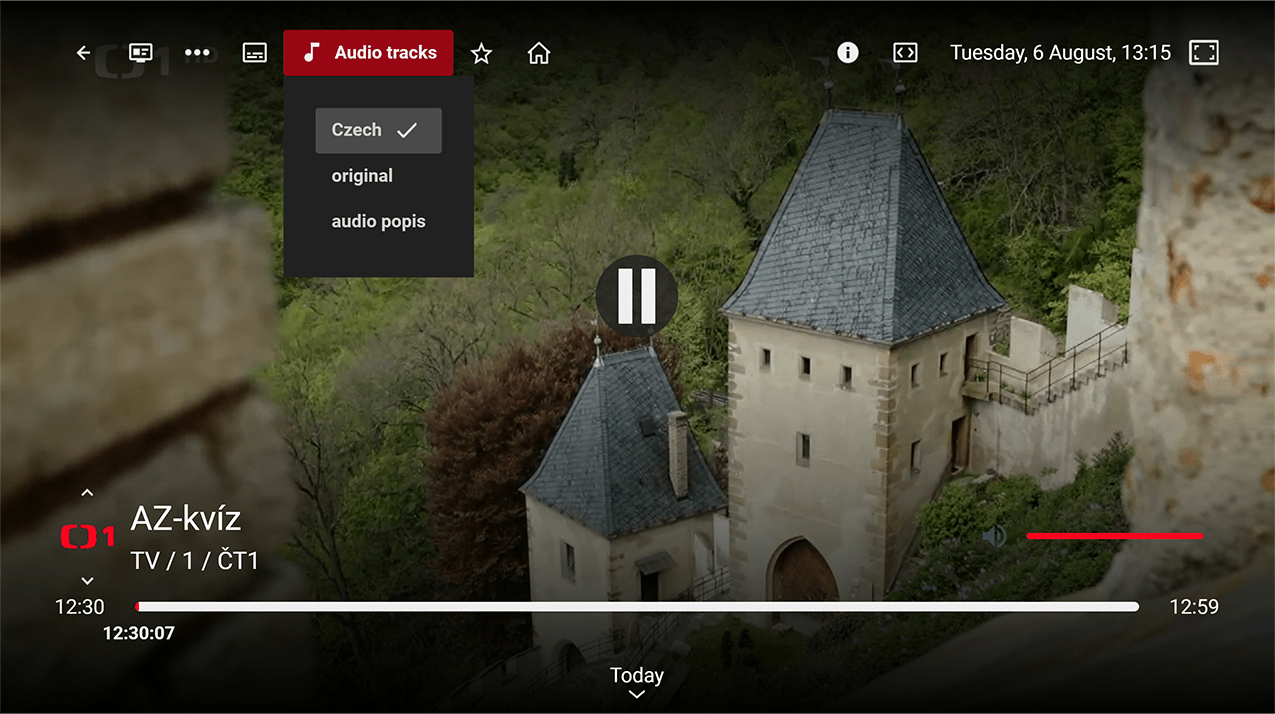 Audio Track Selection:
Audio Track Selection: Users can choose from multiple audio tracks available within the stream.

 Content Bookmarks:
Content Bookmarks: Users can add bookmarks to specific movie moments. A single movie can have multiple bookmarks.
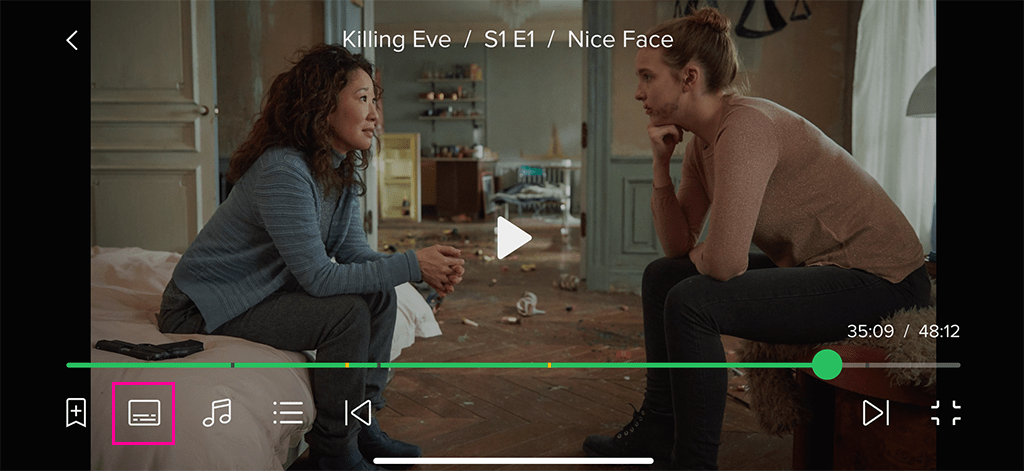
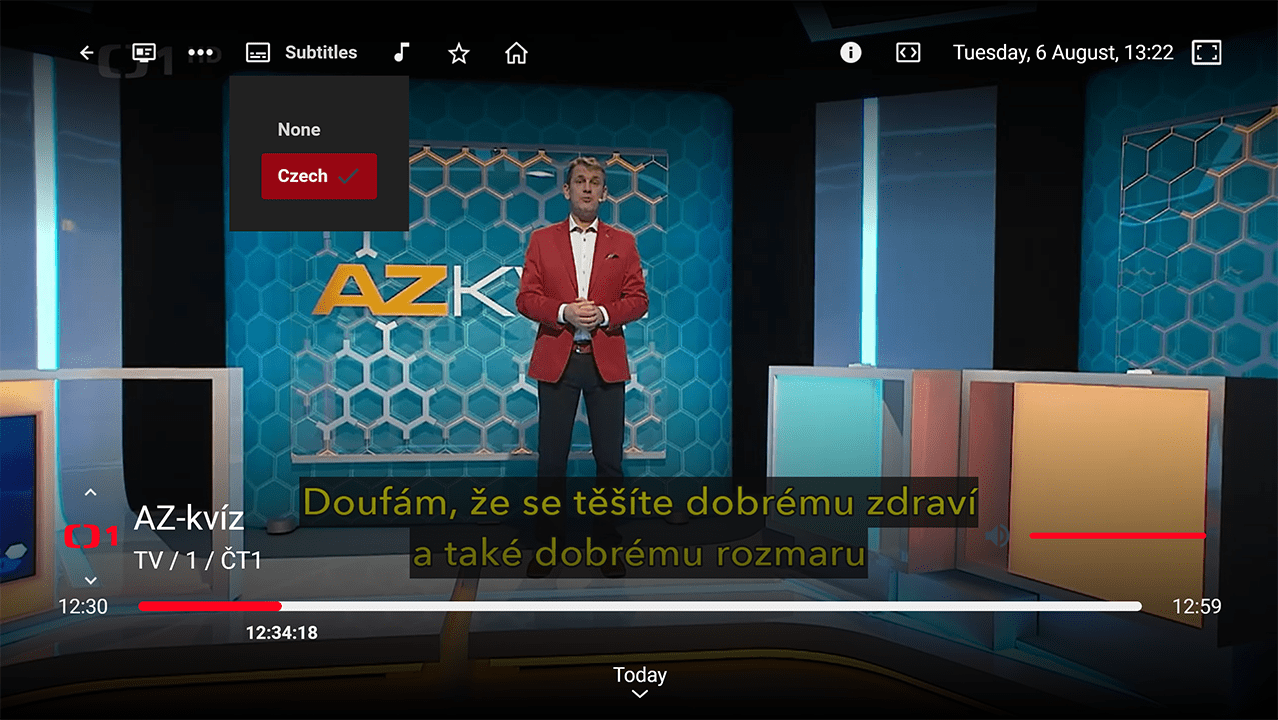 Subtitles and Teletext Display:
Subtitles and Teletext Display: Apps can display subtitles and teletext in various formats, including DVD, DVB, SSA/ASS, SRT, WebVTT, CEA-608/708 Closed Captions, SMPTE-TT, and Teletext. Supported formats may vary by device.
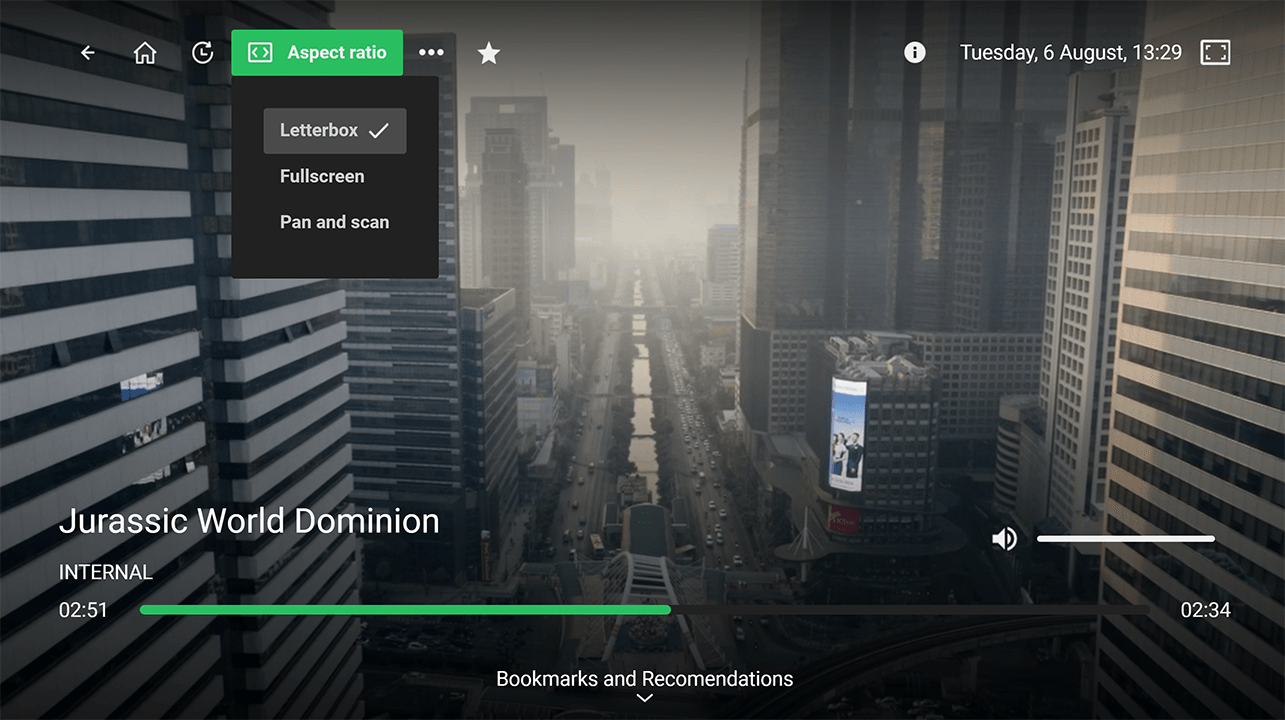 Aspect Ratio Options:
Aspect Ratio Options: Enables users to align the content frame’s aspect ratio with their device’s screen.
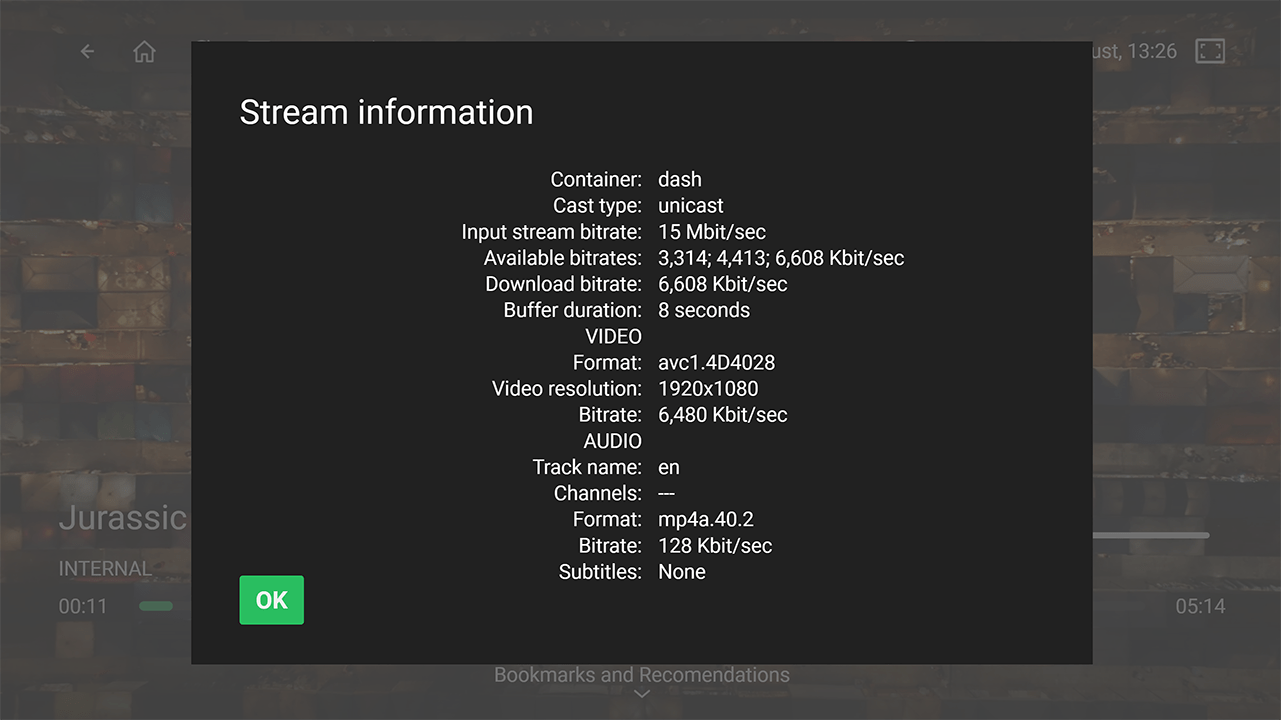 Stream Details:
Stream Details: Depending on the stream type, users can view information such as the current bitrate, the number of decoding errors, and other relevant details that may be helpful for troubleshooting and contacting technical support. Available for the large-screen apps only.
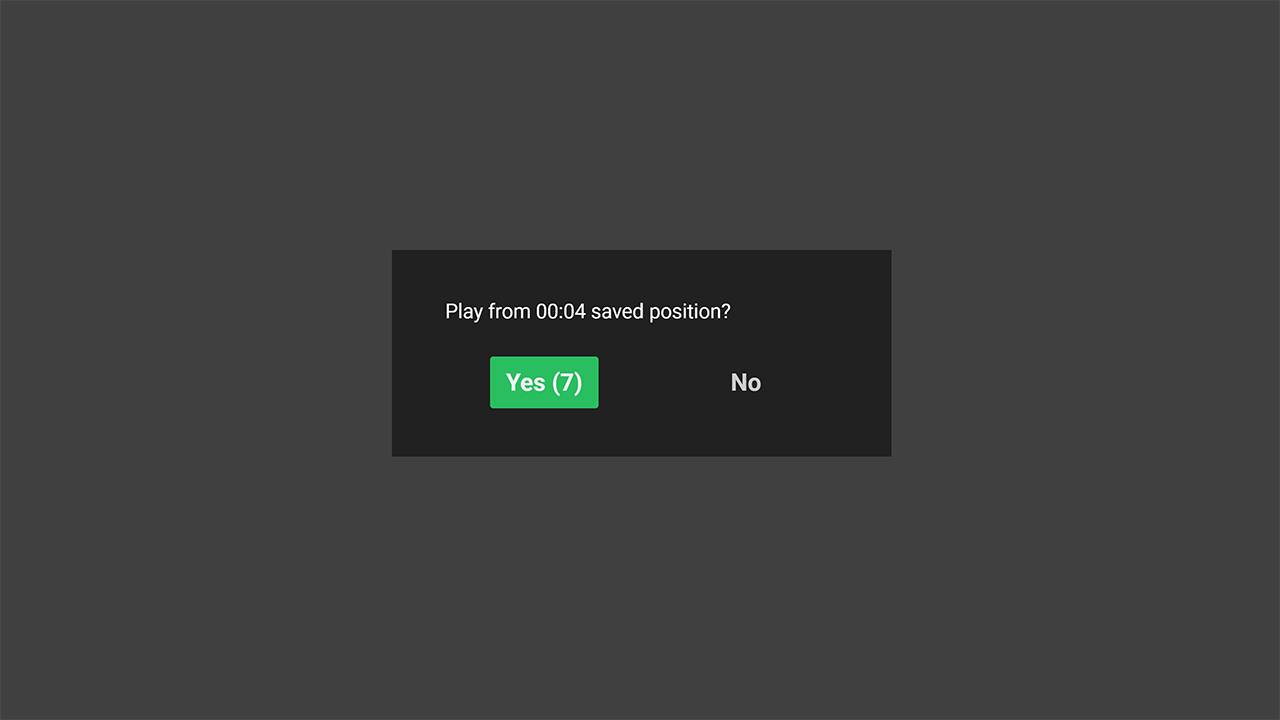 Playback from a Saved Position:
Playback from a Saved Position: Apps remember where a user stopped watching a movie or program and provide the option to resume from that point or start over.

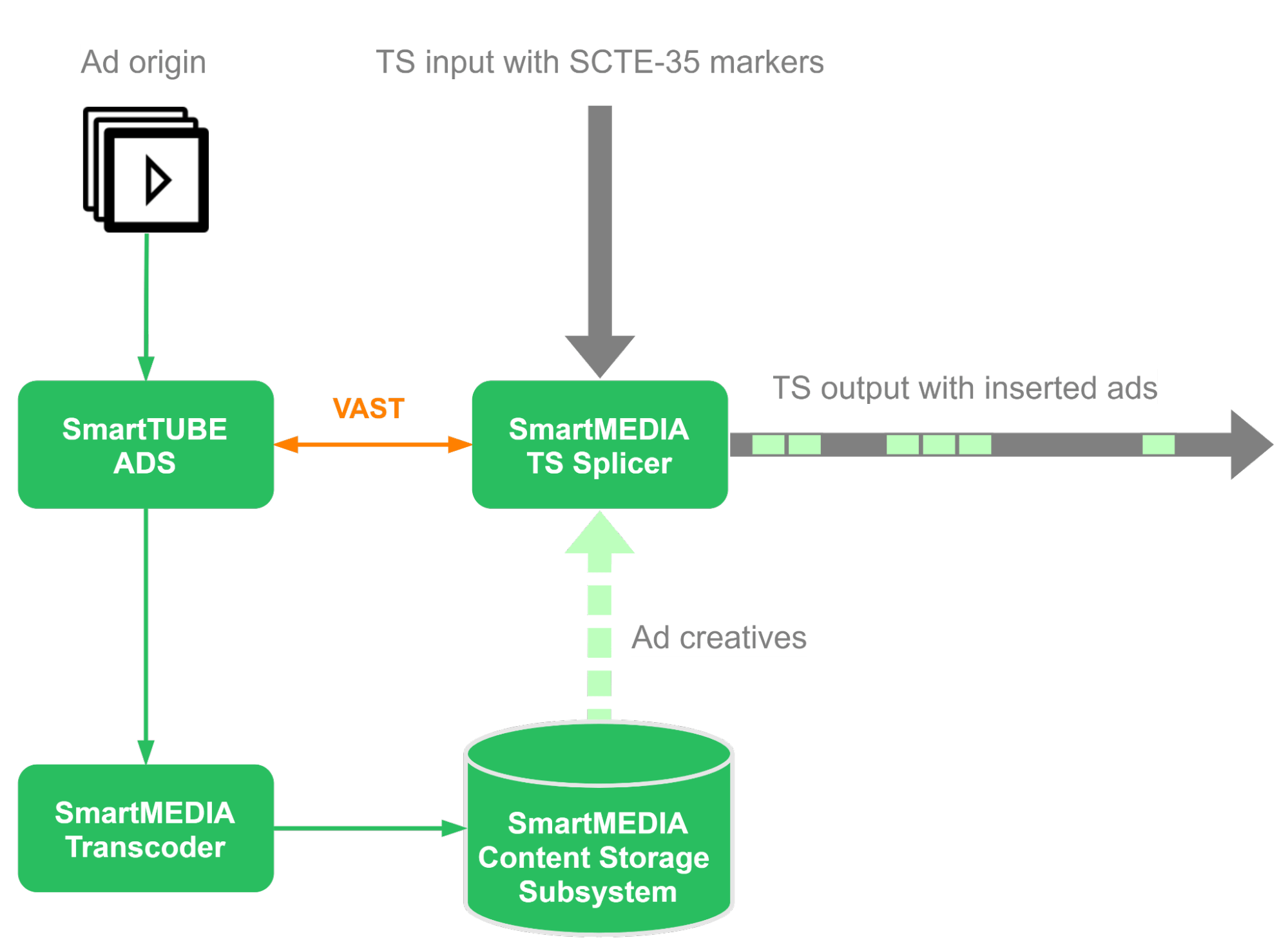
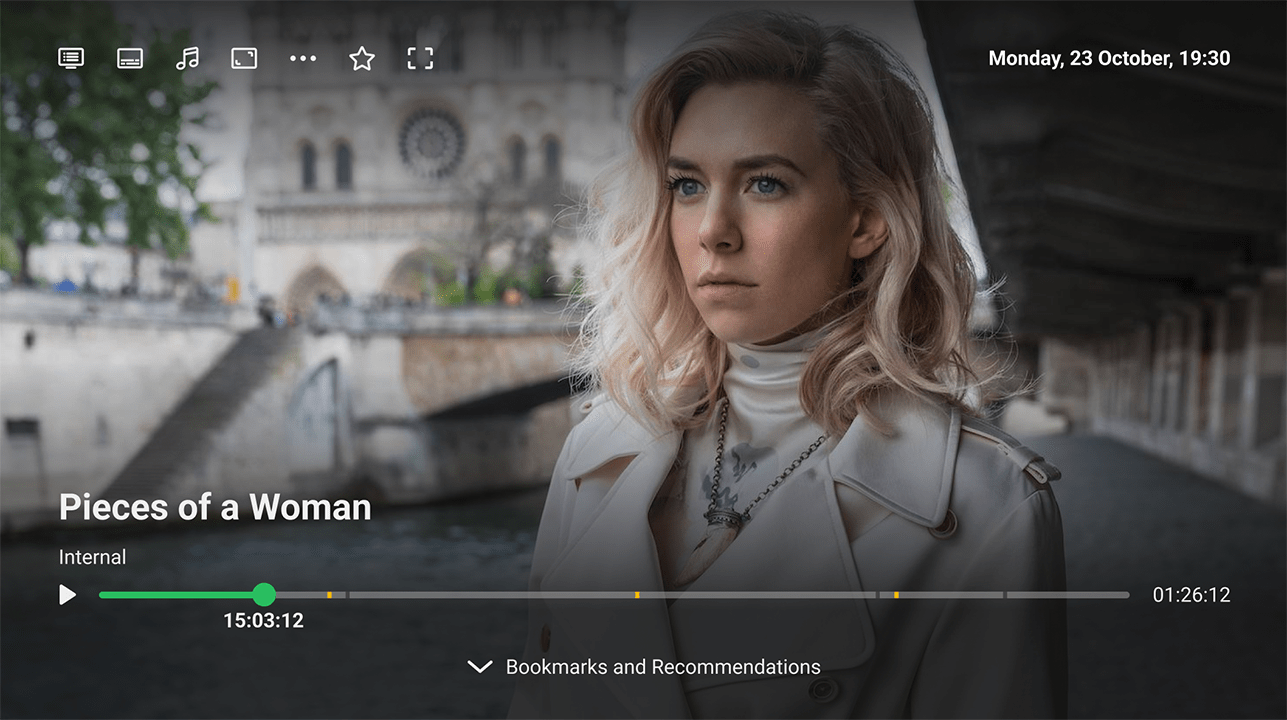 Processing of Ad Inserts:
Processing of Ad Inserts: The app for large-screen devices can detect the start/end marks of ad inserts within the stream. It can handle these ads in different ways, such as preventing users from rewinding during catch-up playback. Additionally, the media player can work with VAST servers within the AVoD service.
Content Purchase and Subscriptions
SmartTUBE Apps offers users a range of features to manage service subscriptions, purchase content, and stay updated on options that enhance their service experience:
- Service Management Menu: Users can view and manage available services, including adding or canceling subscriptions, along with detailed information about offered content and terms.
- Subscription Recommendations: The app highlights both current and additional subscription options, with non-subscribed channels clearly marked and easily accessible for purchase.
- In-App Purchases: Apps for STB and iOS/iPadOS devices allow the purchase of subscriptions to service packages and TVoD content directly in the app interface. Purchases on the iOS/iPadOS app are made through the Apple App Store..
- Purchase History: Subscribers can track their transactions in the ‘Settings’ menu.
Screen Sharing
The Screen Sharing feature allows users to effortlessly transfer their streaming session between devices, such as from a mobile device to a Smart TV or STB, and vice versa. The SmartTUBE platform supports the following technologies to implement the Screen Sharing feature:
- Apple AirPlay: Enables screen sharing from SmartTUBE iOS Mobile App to other devices that support AirPlay 2 technology.
- Google Chromecast: Enables screen sharing from SmartTUBE iOS/Android Mobile App to the Google Chromecast devices and TVs with built-in Chromecast support.
- SmartLabs Screen Sharing: A proprietary technology enabling user to transfer streaming between devices using SmartTUBE Apps. Users can continue watching a movie or TV channel on a mobile device or move content from a mobile device to a large screen while maintaining the current position. After transferring, playback can be controlled remotely from the mobile device.
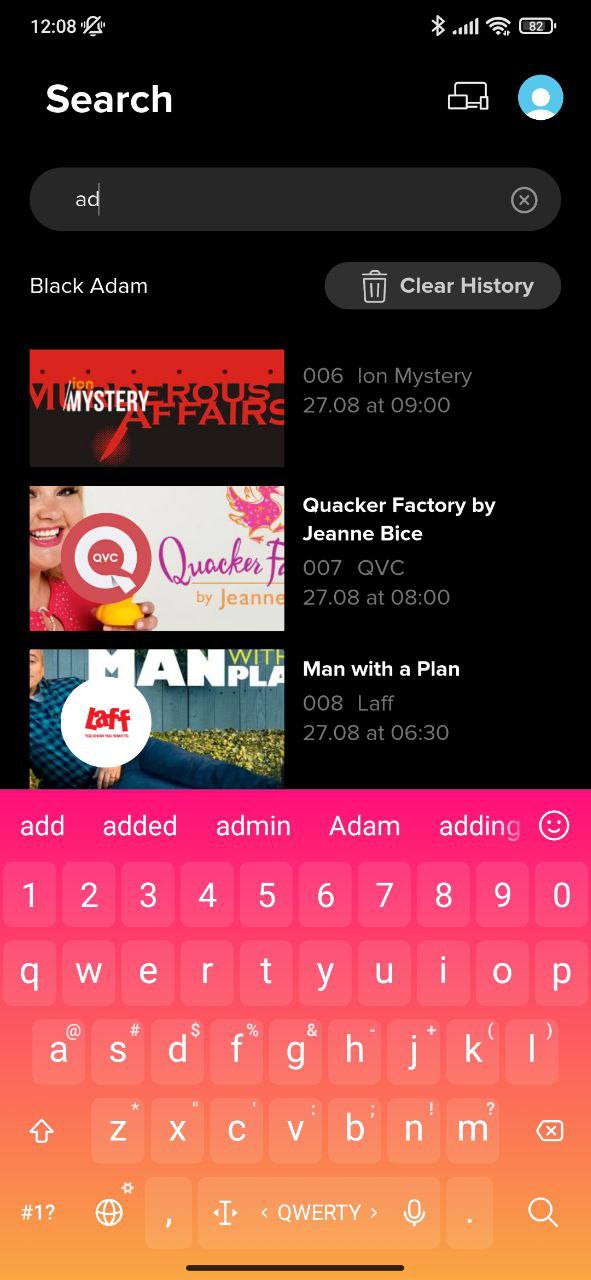
Content Search Screen
SmartTUBE Apps allow users to search through all content types, including TV programs, movies, and external services like YouTube. The search is performed by title (in the current app’s UI language and original title) and description, with suggestions appearing as user type. The Apps support multilingual keyboards and shows structured results for various content types on the same screen.
Displaying Operator Messages
The operator can send subscribers messages that they may open immediately or later in the message history. The message can contain both text and images. Urgent messages are displayed as a full screen window. Watermark messages are overlaid on top of the video stream.
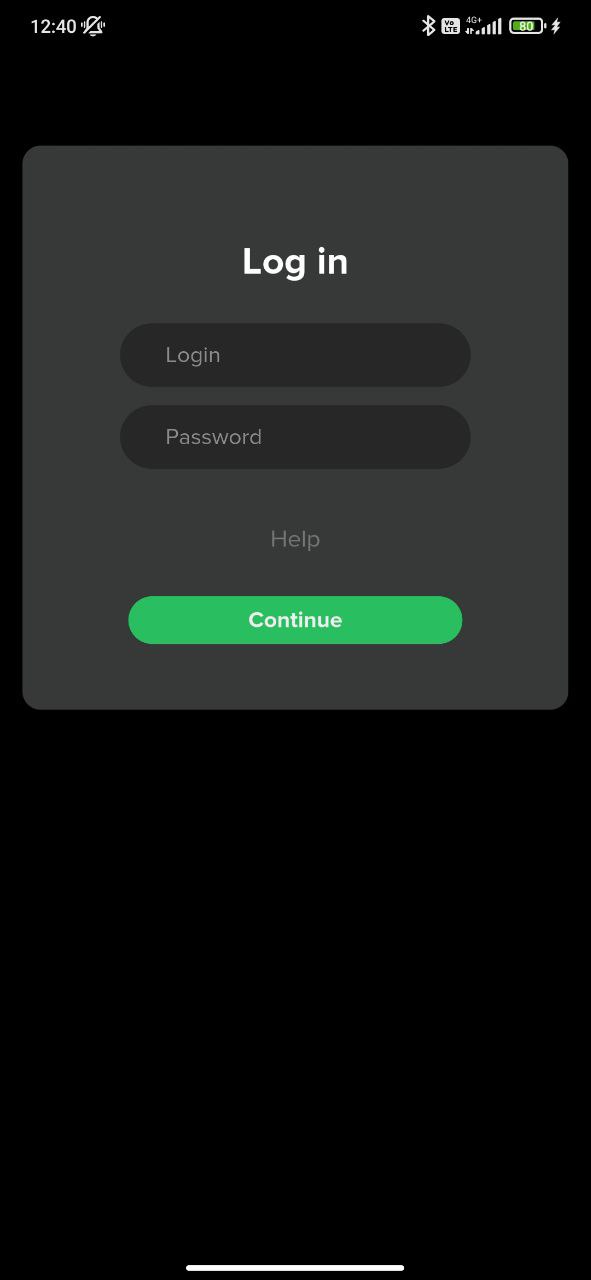
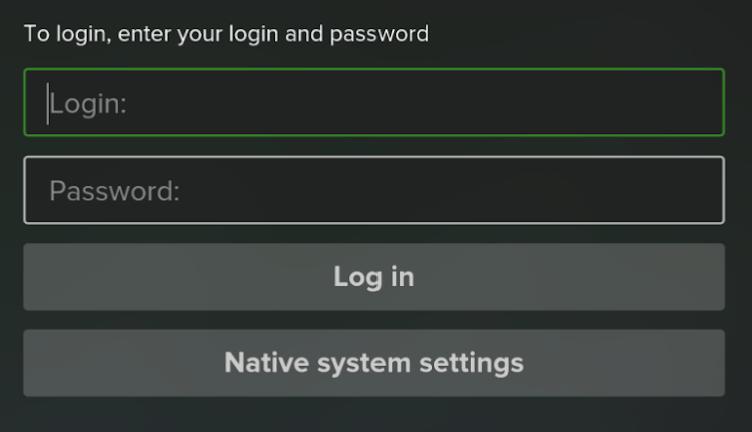
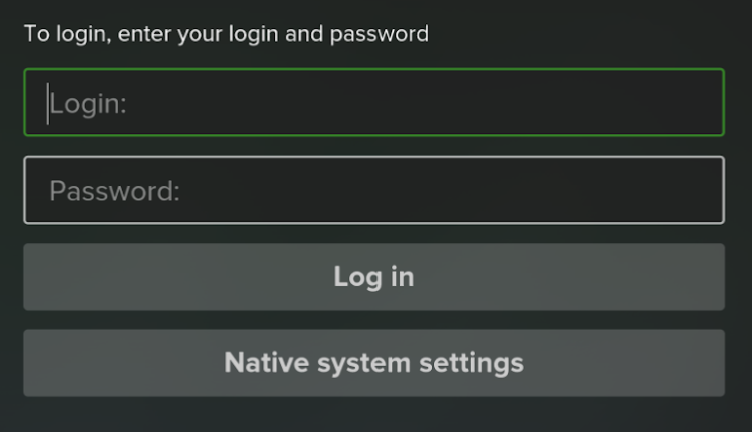
Logging In
Depending on the operator’s settings, subscribers can access services by logging in with or without username and password entry. New users may also be offered a trial period to explore the services and app features.
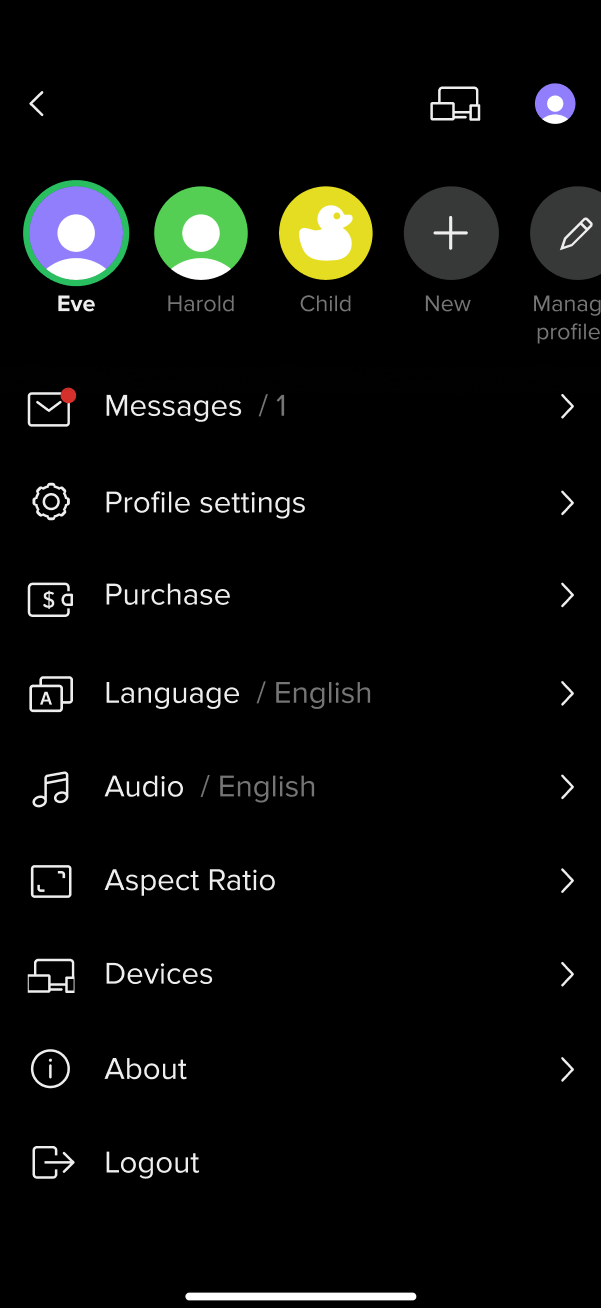
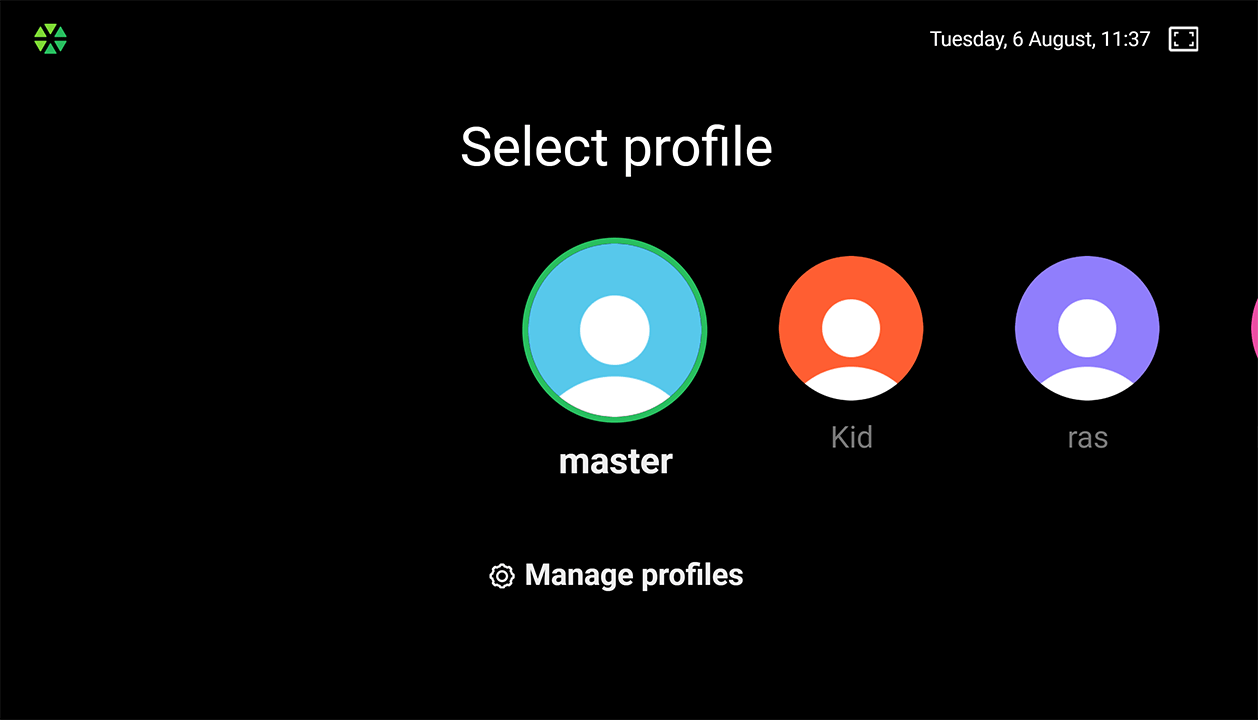
User Profiles
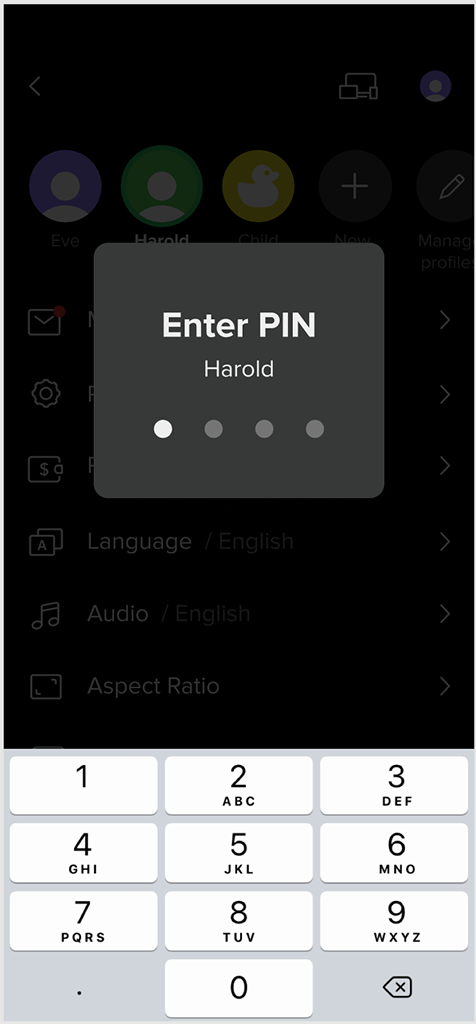
If multiple users share an account, they can create personal Profiles to customize settings like parental controls, channel sorting, and content restrictions. Profiles are shared across all devices and can be PIN protected. The master Profile can manage other profiles. This helps prevent unauthorized access to paid or adult content by minors and provides personalized content recommendations.
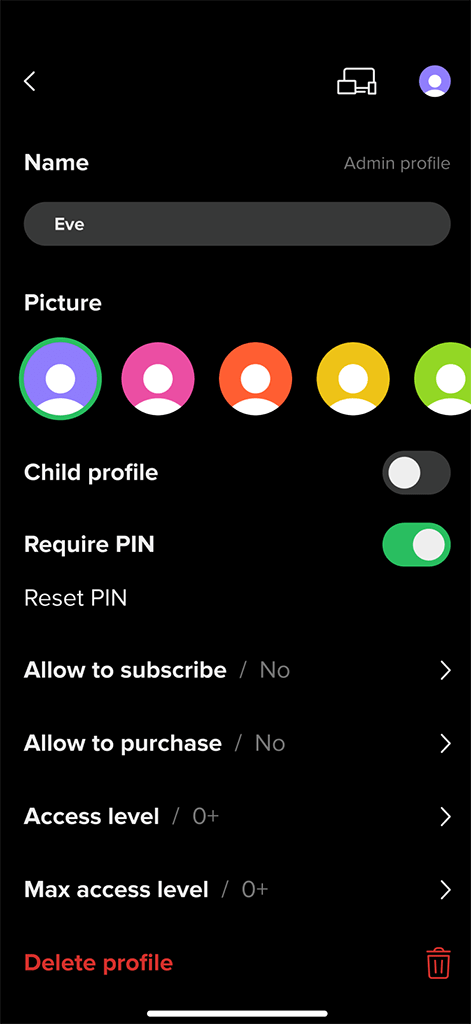
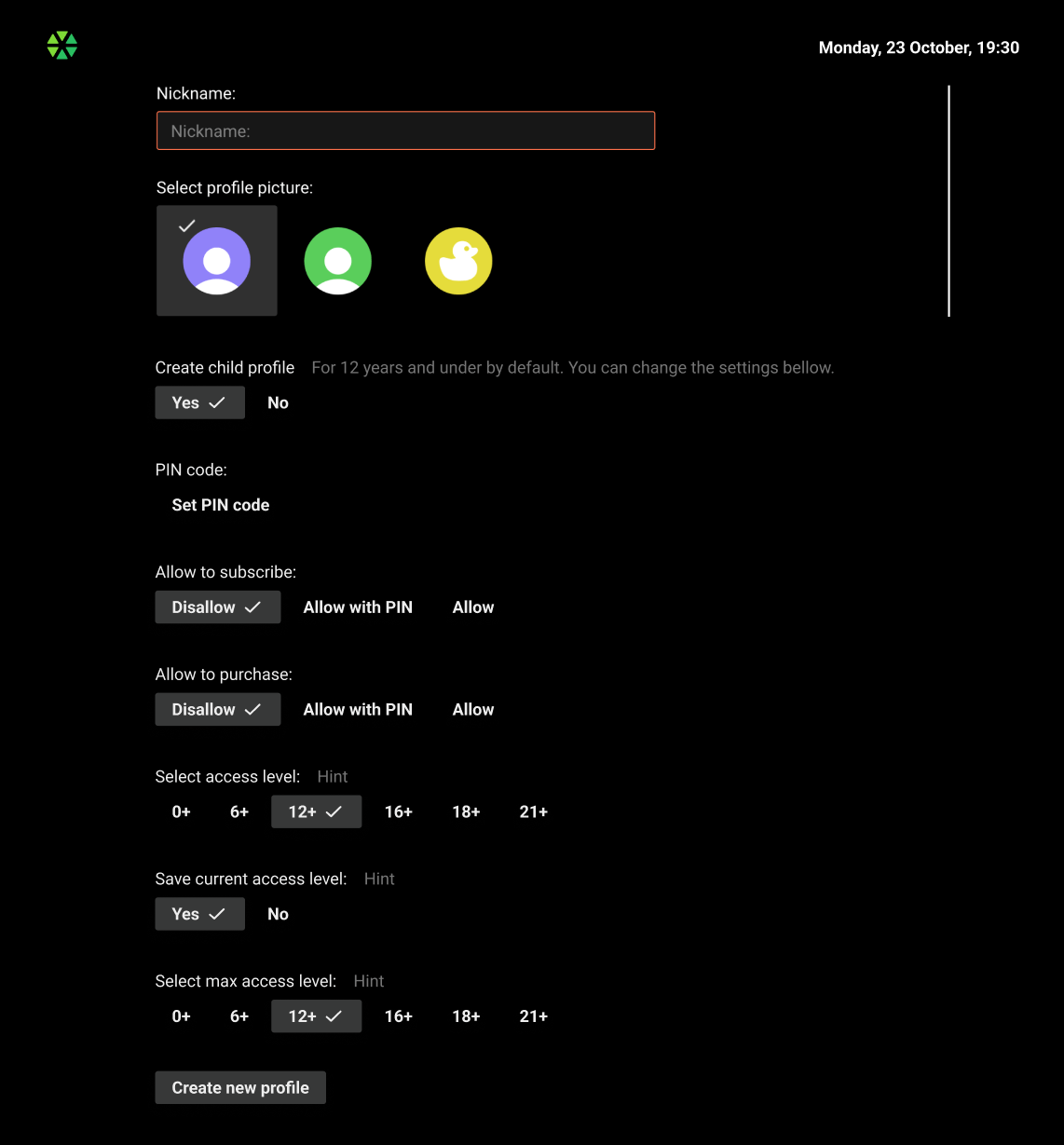
Profile general settings
Kids profile gives parents control over their children’s viewing experience. In addition to the maximum age level for TV channels and VOD content, the Kids profile allows to manage the downtime interval and the daily viewing limit.
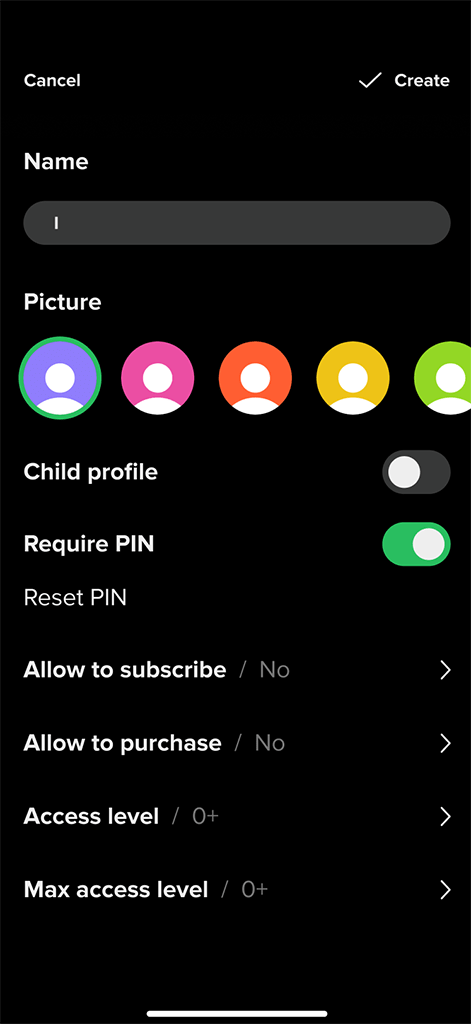
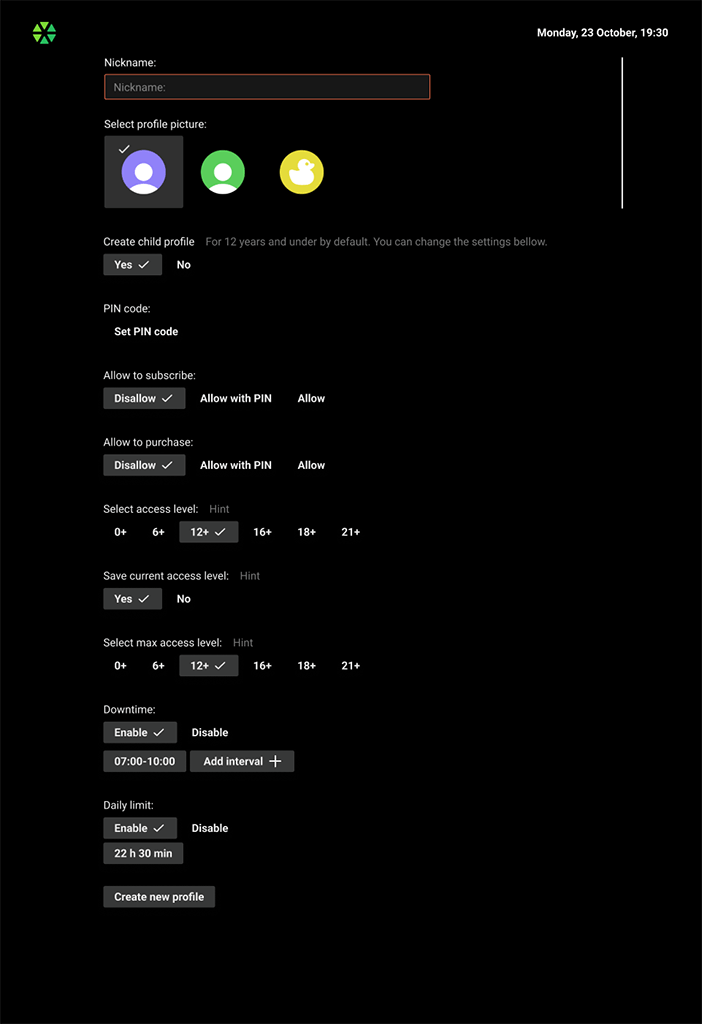
Kids profile settings
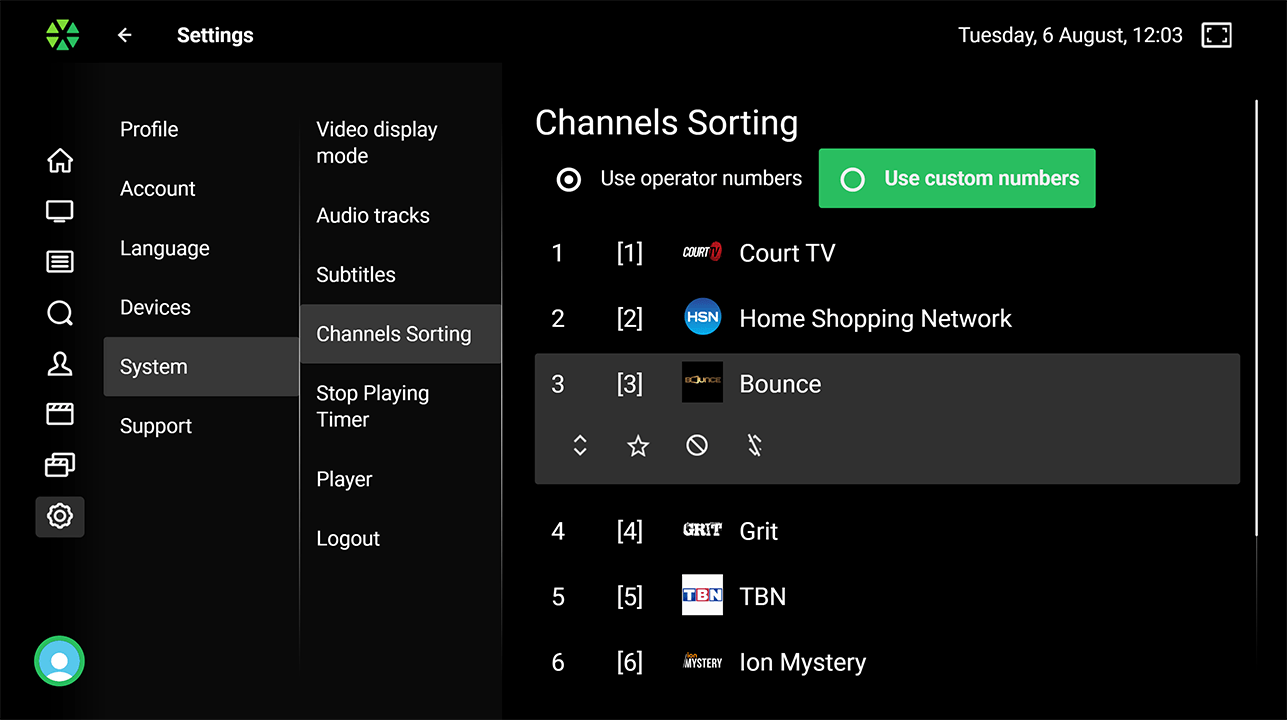
System Settings
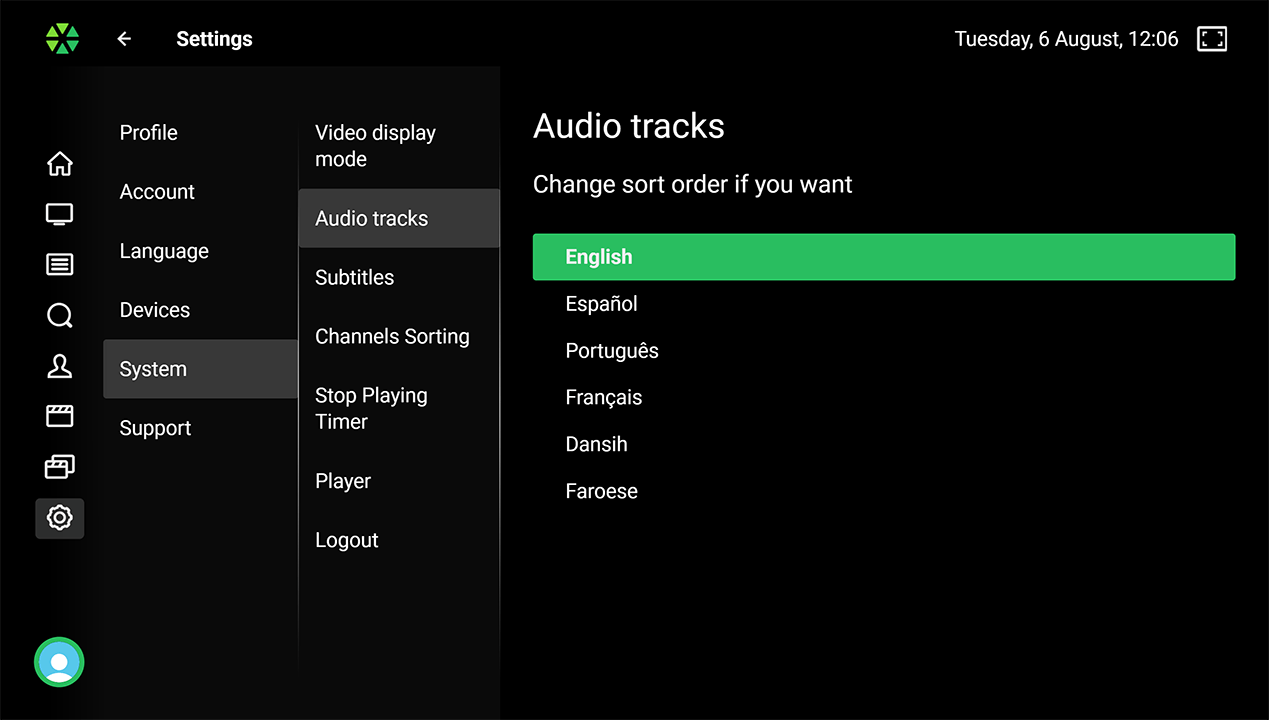
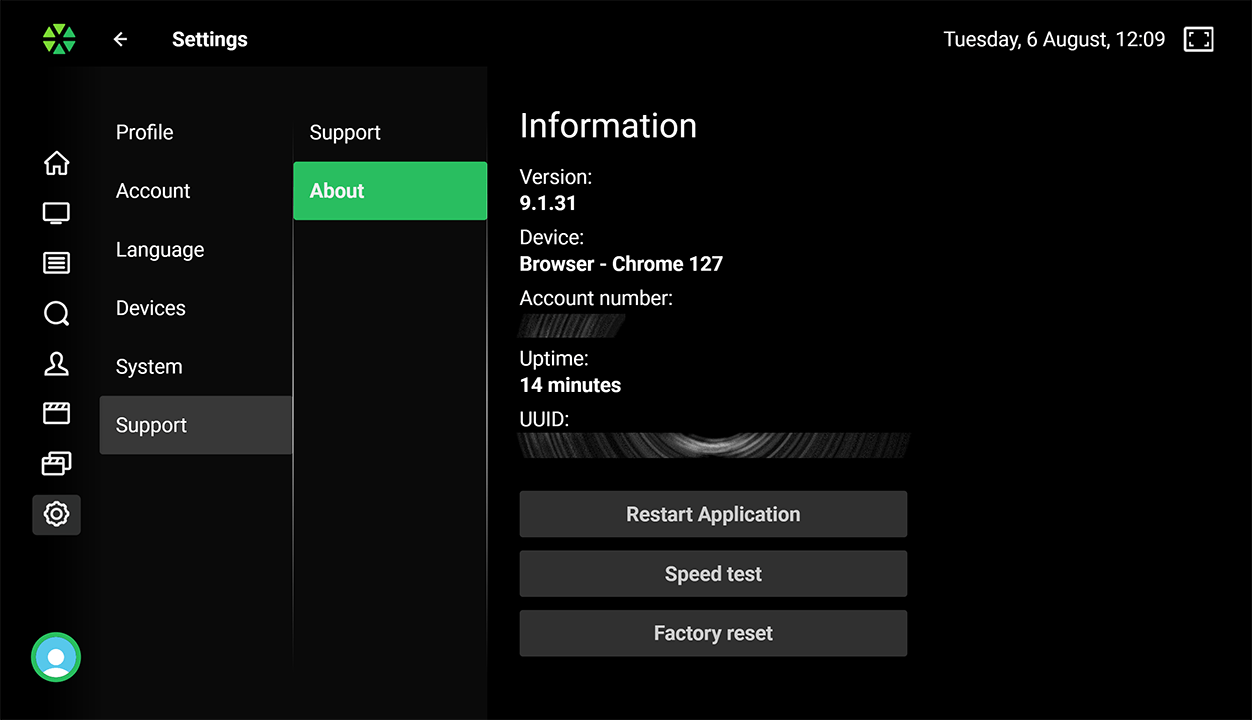
Users can access various system settings, including time-zone correction, UI language, audio/subtitle language prioritization, timer to stop playback when idle, video aspect ratio, and player menu auto-hide timeout. Support page provides information for contacting operator and sending reports for technical analysis.
STB users have additional options:
- Reset to factory settings
- Firmware update
- Standby timer
- Video/audio output format
- Network settings
Supported Devices
SmartTUBE solution supports a wide range of devices, allowing IPTV / OTT operators to reach a larger audience. The list of supported devices can be expanded through integration work. Below are the device requirements. These requirements do not include restrictions related to the use of various protocols and formats of video delivery (HLS, DASH, etc.), CAS/DRM systems, and other restrictions related to the hardware and software implementation of the listed devices by their manufacturers.
Linux based STB
To run SmartTUBE App on STB using a Linux kernel OS, you need to have SmartSDK. At the moment SmartSDK is supported on hardware platforms HiSilicon, STMicroelectronics, Amlogic, Broadcom, Sigma Designs from STB manufacturers such as SmartLabs, Albis, Arris, and others. To clarify the list of supported hardware platforms and integration options, please contact SmartLabs representatives.
Android based STB and Android TV
- Supported OS Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and Android TV v9.0 or later.
- The devices must comply with the Android Compatibility Definition Document (CDD) requirements.
- SmartTUBE App on AOSP devices can be installed as a Launcher.
iOS/iPadOS Devices
- iPad with iOS 12 or later
- iPhone with iOS 12 or later
Android Devices
The devices must comply with the Android Compatibility Definition Document (CDD) requirements.
- Tablet PC with Android 5.0 Lollipop (API Level 21) or later
- Smartphones with Android 5.0 Lollipop (API Level 21) or later
LG Smart TV
- webOS 4.0 and higher (generally models from 2018 and onward)
- Support for earlier platforms, including Netcast and webOS versions prior to 4.0, may be available upon special request. However, such support is subject to technical feasibility and may depend on factors such as the DRM system, streaming protocols used, and other implementation specifics.
Samsung Smart TV
- Tizen OS 3.0 and higher (generally models from 2017 and onward)
- The Samsung App Store generally supports app publishing for devices from the five most recent model years. Support for earlier models may be available through a separate agreement with Samsung.
Hisense Smart TV
- VIDAA OS 1.2 and higher (generally models from 2021 and onward).
Smart TV with Whale OS
Whale OS (zeasn.com) is an operating system for Smart TV, which is now integrated into the products of many world-famous brands, including Philips, TCL, Haier, AOC, Sharp, BenQ, Konka, Changhong, NovaTek, Amazon, Google, Alibaba, Huawei, DSP Group, and etc.
Amazon Fire TV
- Amazon Fire TV Stick Lite
- Amazon Fire TV Stick
- Amazon Fire TV Stick 4K
- Amazon Fire TV Stick 4K Max
- Amazon Fire TV Cube
Web Browsers
| Web Browser |
OS |
Minimal version supported by the app |
Minimal version supported by the app with Widevine DRM playback |
| Google Chrome |
Windows / Linux / MacOS |
⩾ 69 |
⩾ 128 |
| Mozilla Firefox |
Windows / Linux / MacOS |
⩾ 100 |
⩾ 100 |
| Microsoft Edge |
Windows |
all |
⩾ 88 |
| Apple Safari |
MacOS |
⩾ 11 |
Safari does not support Widevine DRM |
We strongly recommend using installations with Widevine DRM enabled. Support for other web browsers is on request.
Support for Device Features
| |
Linux STB |
Android STB |
iOS |
Android 5.0
and later |
Samsung
SmartTV (Tizen) |
LG
Smart TV (WebOS) |
| Multicast |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
| Voice search/input |
Yes
(using BT RCU) |
Yes
(using BT RCU) |
Yes
(Native) |
Yes
(Native) |
Yes
(Native) |
Yes
(Native) |
| External applications |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
No |
| AirPlay |
No |
No |
Yes |
No |
No |
No |
| Chromecast Sender |
No |
No |
Yes
|
Yes |
No |
No |
| Android/iOS native PiP |
No |
No |
Yes* |
Yes |
No |
No |
| Offline content |
No |
No |
Yes
|
Roadmap |
No |
No |
* The PiP feature is available on iOS devices for HLS streams only.
Support for Content Delivery Protocols and DRM Systems
| Device model / Technology |
Widevine / DASH |
PlayReady / DASH |
FairPlay / HLS |
| Samsung Legacy (2012–2015 models) |
No |
No |
No |
| Samsung Tizen (2015 and 2016 models without software updates installed) |
No |
Yes |
No |
| Samsung Tizen (2016 models with software updates installed) |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
| Samsung Tizen (2017 models and later) |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
| LG NetCast (models until 2014) |
No |
No |
No |
| LG WebOS 2.x (models until 2016) |
No |
No |
No |
| LG WebOS 3.5 and later (2017 models and later) |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
| SmartLabs STB, Android 5.0 and later |
Yes |
No |
No |
| iOS 12 and later |
Not recommended |
No |
Yes |
Change Log
SmartTUBE App for iOS and iPadOS 9.x
- The supported iOS version is changed from iOS 11 to 12.